| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Graphs of Exponential Functions , we saw how creating a graphical representation of an exponential model gives us another layer of insight for predicting future events. How do logarithmic graphs give us insight into situations? Because every logarithmic function is the inverse function of an exponential function, we can think of every output on a logarithmic graph as the input for the corresponding inverse exponential equation. In other words, logarithms give the cause for an effect .
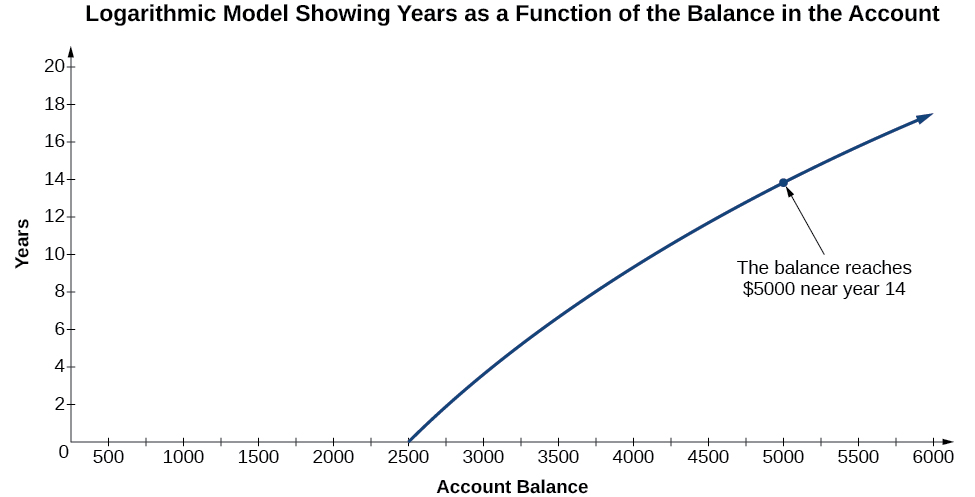
To illustrate, suppose we invest in an account that offers an annual interest rate of compounded continuously. We already know that the balance in our account for any year can be found with the equation
But what if we wanted to know the year for any balance? We would need to create a corresponding new function by interchanging the input and the output; thus we would need to create a logarithmic model for this situation. By graphing the model, we can see the output (year) for any input (account balance). For instance, what if we wanted to know how many years it would take for our initial investment to double? [link] shows this point on the logarithmic graph.
In this section we will discuss the values for which a logarithmic function is defined, and then turn our attention to graphing the family of logarithmic functions.
Before working with graphs, we will take a look at the domain (the set of input values) for which the logarithmic function is defined.
Recall that the exponential function is defined as for any real number and constant where
In the last section we learned that the logarithmic function is the inverse of the exponential function So, as inverse functions:
Transformations of the parent function behave similarly to those of other functions. Just as with other parent functions, we can apply the four types of transformations—shifts, stretches, compressions, and reflections—to the parent function without loss of shape.
In Graphs of Exponential Functions we saw that certain transformations can change the range of Similarly, applying transformations to the parent function can change the domain . When finding the domain of a logarithmic function, therefore, it is important to remember that the domain consists only of positive real numbers . That is, the argument of the logarithmic function must be greater than zero.
For example, consider This function is defined for any values of such that the argument, in this case is greater than zero. To find the domain, we set up an inequality and solve for
In interval notation, the domain of is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?