| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
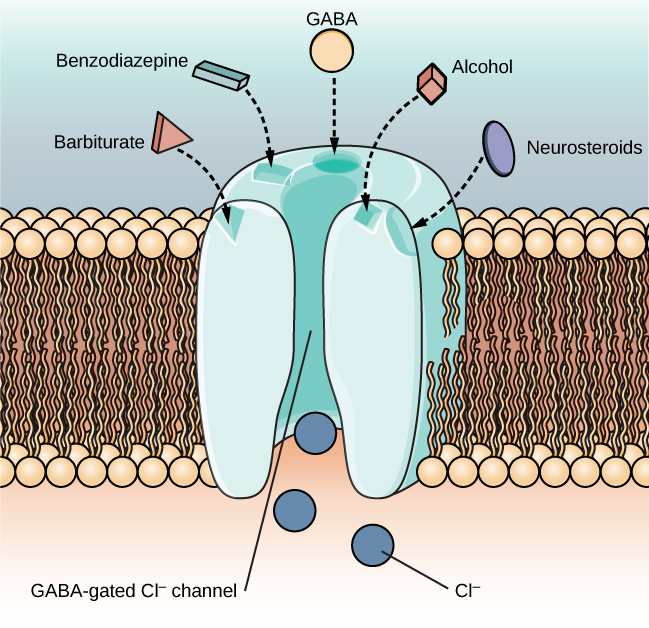
Ethanol, which we commonly refer to as alcohol, is in a class of psychoactive drugs known as depressants ( [link] ). A depressant is a drug that tends to suppress central nervous system activity. Other depressants include barbiturates and benzodiazepines. These drugs share in common their ability to serve as agonists of the gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter system. Because GABA has a quieting effect on the brain, GABA agonists also have a quieting effect; these types of drugs are often prescribed to treat both anxiety and insomnia.
Acute alcohol administration results in a variety of changes to consciousness. At rather low doses, alcohol use is associated with feelings of euphoria. As the dose increases, people report feeling sedated. Generally, alcohol is associated with decreases in reaction time and visual acuity, lowered levels of alertness, and reduction in behavioral control. With excessive alcohol use, a person might experience a complete loss of consciousness and/or difficulty remembering events that occurred during a period of intoxication (McKim&Hancock, 2013). In addition, if a pregnant woman consumes alcohol, her infant may be born with a cluster of birth defects and symptoms collectively called fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) or fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS).
With repeated use of many central nervous system depressants, such as alcohol, a person becomes physically dependent upon the substance and will exhibit signs of both tolerance and withdrawal. Psychological dependence on these drugs is also possible. Therefore, the abuse potential of central nervous system depressants is relatively high.
Drug withdrawal is usually an aversive experience, and it can be a life-threatening process in individuals who have a long history of very high doses of alcohol and/or barbiturates. This is of such concern that people who are trying to overcome addiction to these substances should only do so under medical supervision.
Stimulants are drugs that tend to increase overall levels of neural activity. Many of these drugs act as agonists of the dopamine neurotransmitter system. Dopamine activity is often associated with reward and craving; therefore, drugs that affect dopamine neurotransmission often have abuse liability. Drugs in this category include cocaine, amphetamines (including methamphetamine), cathinones (i.e., bath salts), MDMA (ecstasy), nicotine, and caffeine.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?