| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Psychologists striving to understand the human mind may study the nervous system. Learning how the cells and organs (like the brain) function, help us understand the biological basis behind human psychology. The nervous system is composed of two basic cell types: glial cells (also known as glia) and neurons. Glial cells, which outnumber neurons ten to one, are traditionally thought to play a supportive role to neurons, both physically and metabolically. Glial cells provide scaffolding on which the nervous system is built, help neurons line up closely with each other to allow neuronal communication, provide insulation to neurons, transport nutrients and waste products, and mediate immune responses. Neurons , on the other hand, serve as interconnected information processors that are essential for all of the tasks of the nervous system. This section briefly describes the structure and function of neurons.
Neurons are the central building blocks of the nervous system, 100 billion strong at birth. Like all cells, neurons consist of several different parts, each serving a specialized function ( [link] ). A neuron’s outer surface is made up of a semipermeable membrane . This membrane allows smaller molecules and molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it, while stopping larger or highly charged molecules.
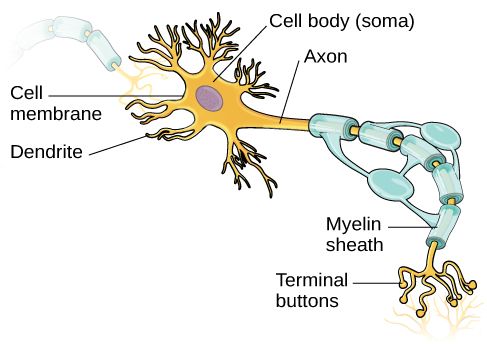
The nucleus of the neuron is located in the soma , or cell body. The soma has branching extensions known as dendrites . The neuron is a small information processor, and dendrites serve as input sites where signals are received from other neurons. These signals are transmitted electrically across the soma and down a major extension from the soma known as the axon , which ends at multiple terminal buttons . The terminal buttons contain synaptic vesicles that house neurotransmitters , the chemical messengers of the nervous system.
Axons range in length from a fraction of an inch to several feet. In some axons, glial cells form a fatty substance known as the myelin sheath , which coats the axon and acts as an insulator, increasing the speed at which the signal travels. The myelin sheath is crucial for the normal operation of the neurons within the nervous system: the loss of the insulation it provides can be detrimental to normal function. To understand how this works, let’s consider an example. Multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disorder, involves a large-scale loss of the myelin sheath on axons throughout the nervous system. The resulting interference in the electrical signal prevents the quick transmittal of information by neurons and can lead to a number of symptoms, such as dizziness, fatigue, loss of motor control, and sexual dysfunction. While some treatments may help to modify the course of the disease and manage certain symptoms, there is currently no known cure for multiple sclerosis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?