| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The purpose of a detector is to monitor the carrier gas as it emerges from the column and to generate a signal in response to variation in its composition due to eluted components. As it transmits physical signal into recordable electrical signal, it is another crucial part of GC. The requirements of a detector for GC are listed below.
Detectors for GC must respond rapidly to minute concentration of solutes as they exit the column, i.e., they are required to have a fast response and a high sensitivity. Other desirable properties of a detector are: linear response, good stability, ease of operation, and uniform response to a wide variety of chemical species or, alternatively predictable and selective response to one or more classes of solutes.
GC system originally used paper chart readers, but modern system typically uses an online computer, which can track and record the electrical signals of the separated peaks. The data can be later analyzed by software to provide the information of the gas mixture.
An ideal separation is judged by resolution, efficiency, and symmetry of the desired peaks, as illustrated by [link] .
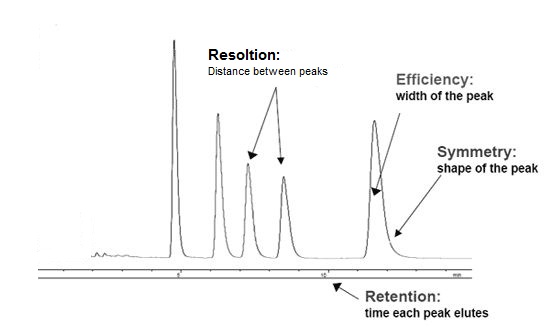
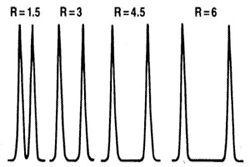
Resolution can be simply expressed as the distance on the output trace between two peaks. The highest possible resolution is the goal when developing a separation method. Resolution is defined by the R value, [link] , which can be expressed mathamatically, [link] , where k is capacity, α is selectivity, and N is the number of theoretical plates. An R value of 1.5 is defined as being the minimum required for baseline separation, i.e., the two adjacent peaks are separated by the baseline. Separation for different R values is illustrated in [link] .
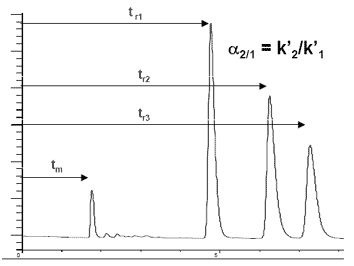
Capacity (k´) is known as the retention factor. It is a measure of retention by the stationary phase. It is calculated from [link] , where t r = retention time of analyte (substance to be analyzed), and t m = retention time of an unretained compound.
Selectivity is related to α, the separation factor ( [link] ). The value of α should be large enough to give baseline resolution, but minimized to prevent waste.
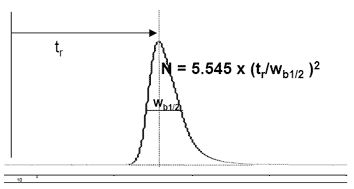
Narrow peaks have high efficiency ( [link] ), and are desired. Units of efficiency are "theoretical plates" (N) and are often used to describe column performance. "Plates" is the current common term for N, is defined as a function of the retention time (t r ) and the full peak width at half maximum (W b1/2 ), EQ.
The symmetry of a peak is judged by the values of two half peak widths, a and b ( [link] ). When a = b , a peak is called symmetric, which is desired. Unsymmetrical peaks are often described as "tailing" or "fronting".

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?