| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Gas chromatography (GC) is a very commonly used chromatography in analytic chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that are gaseous or can be vaporized without decomposition. Because of its simplicity, sensitivity, and effectiveness in separating components of mixtures, gas chromatography is an important tools in chemistry. It is widely used for quantitative and qualitative analysis of mixtures, for the purification of compounds, and for the determination of such thermochemical constants as heats of solution and vaporization, vapor pressure, and activity coefficients. Compounds are separated due to differences in their partitioning coefficient between the stationary phase and the mobile gas phase in the column.
A gas chromatograph ( [link] ) consists of a carrier gas system, a sampling system, a separation system, a detection system, and a data recording system.
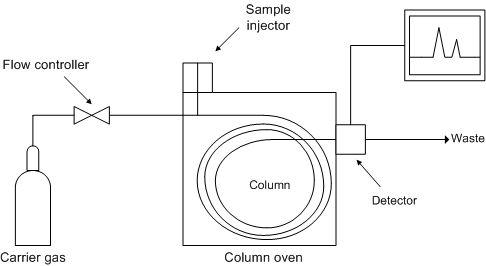
The carrier gas system consists of carrier gas sources, purification, and gas flow control. The carrier gas must be chemically inert. Commonly used gases include nitrogen, helium, argon, and carbon dioxide. The choice of carrier gas often depends upon the type of detector used. A molecular sieve is often contained in the carrier gas system to remove water and other impurities.
An auto sampling system consists of auto sampler, and vaporization chamber. The sample to be analyzed is loaded at the injection port via a hypodermic syringe and it will be volatilized as the injection port is heated up. Typically samples of one micro liter or less are injected on the column. These volumes can be further reduced by using what is called a split injection system in which a controlled fraction of the injected sample is carried away by a gas stream before entering the column.
The separation system consists of columns and temperature controlling oven. The column is where the components of the sample are separated, and is the crucial part of a GC system. The column is essentially a tube that contains different stationary phases have different partition coefficients with analytes,and determine the quality of separation. There are two general types of column: packed ( [link] ) and capillary also known as open tubular ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?