| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate the components in a mixture, and to identify and quantify each component. It was initially discovered as an analytical technique in the early twentieth century and was first used to separate colored compounds. The word chromatography means color writing . It was the botanist M. S. Tswett ( [link] ) who invented this method in around 1900 to study leaf pigments (mainly chlorophyll). He separated the pigments based on their interaction with a stationary phase. In 1906 Tswett published two fundamental papers describing the various aspects of liquid-adsorption chromatography in detail. He also pointed out that in spite of its name, other substances also could be separated by chromatography. The modern high performance liquid chromatography has developed from this separation; the separation efficiency, versatility and speed have been improved significantly.

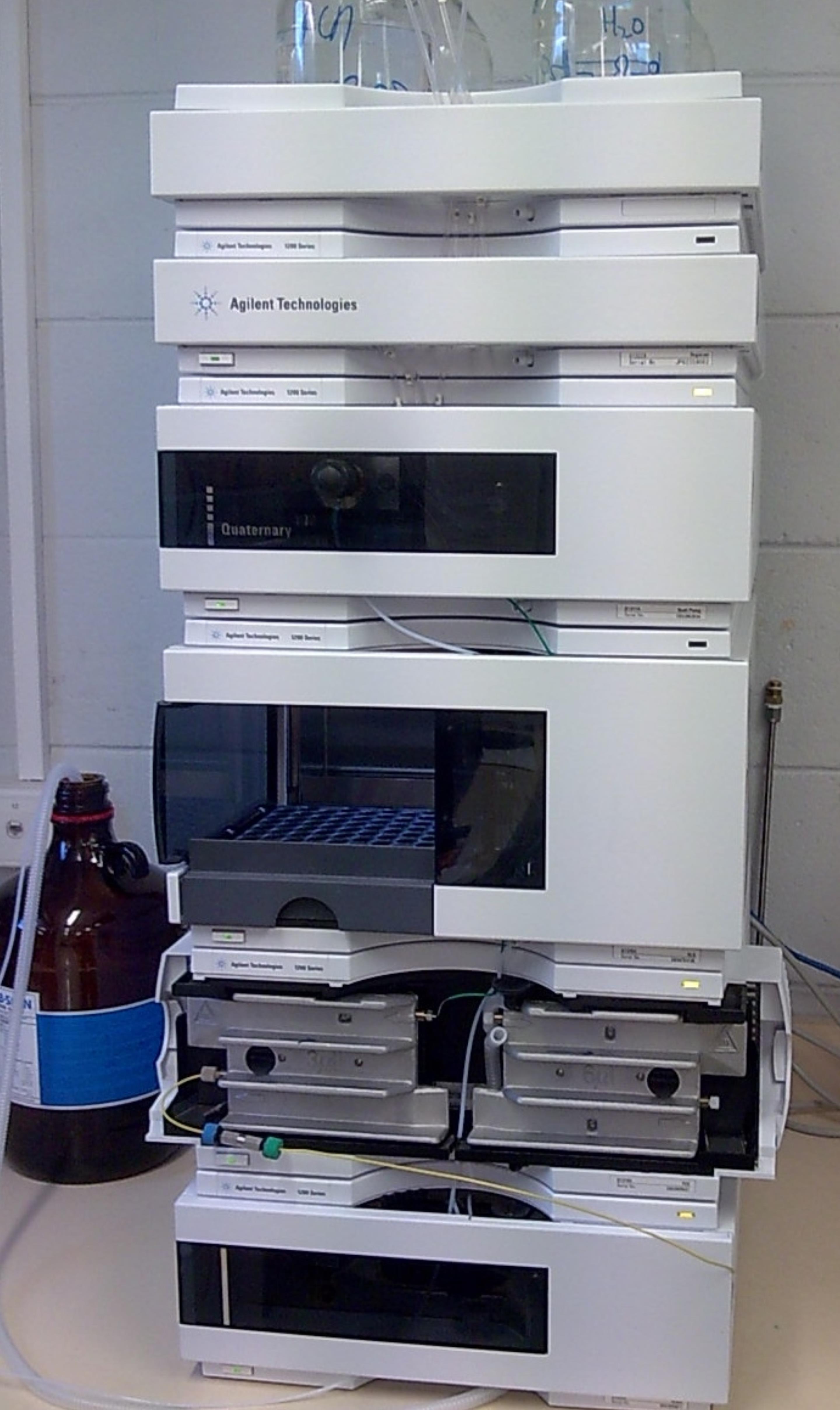
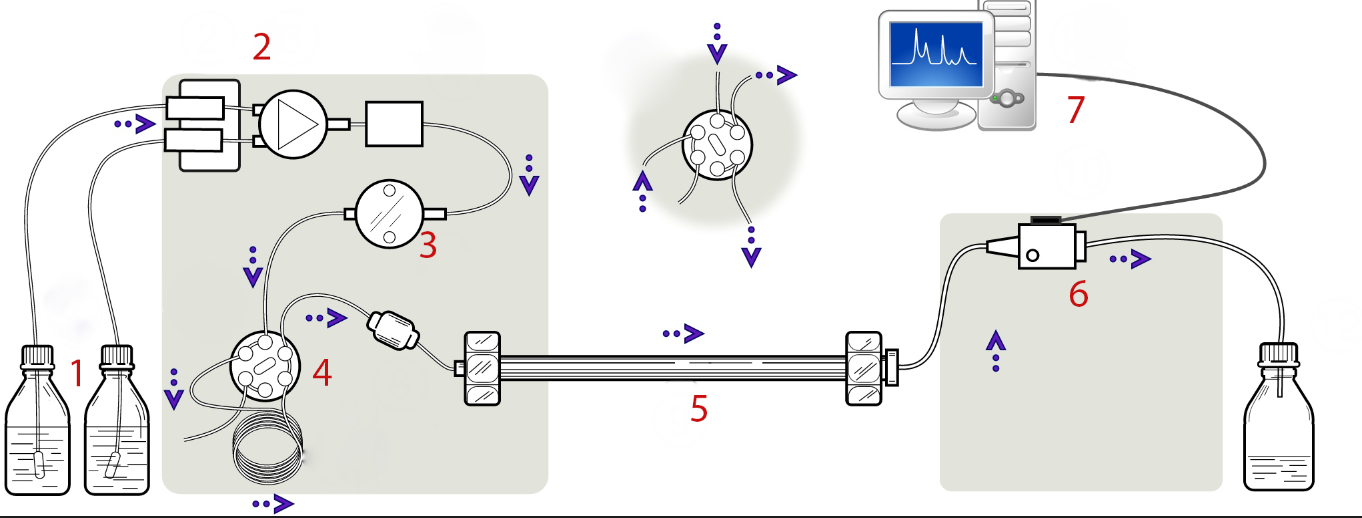
The molecular species subjected to separation exist in a sample that is made of analytes and matrix . The analytes are the molecular species of interest, and the matrix is the rest of the components in the sample. For chromatographic separation, the sample is introduced in a flowing mobile phase that passes a stationary phase . Mobile phase is a moving liquid, and is characterized by its composition, solubility, UV transparency, viscosity, and miscibility with other solvents. Stationary phase is a stationary medium, which can be a stagnant bulk liquid, a liquid layer on the solid phase, or an interfacial layer between liquid and solid. In HPLC, the stationary phase is typically in the form of a column packed with very small porous particles and the liquid mobile phase is moved through the column by a pump. The development of HPLC is mainly the development of the new columns, which requires new particles, new stationary phases (particle coatings), and improved procedures for packing the column. A picture of modern HPLC is shown in [link] .

The major components of a HPLC are shown in [link] . The role of a pump is to force a liquid (mobile phase) through at a specific flow rate (milliliters per minute). The injector serves to introduce the liquid sample into the flow stream of the mobile phase. Column is the most central and important component of HPLC, and the column’s stationary phase separates the sample components of interest using various physical and chemical parameters. The detector is to detect the individual molecules that elute from the column. The computer usually functions as the data system, and the computer not only controls all the modules of the HPLC instrument but it takes the signal from the detector and uses it to determine the retention time, the sample components, and quantitative analysis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?