| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

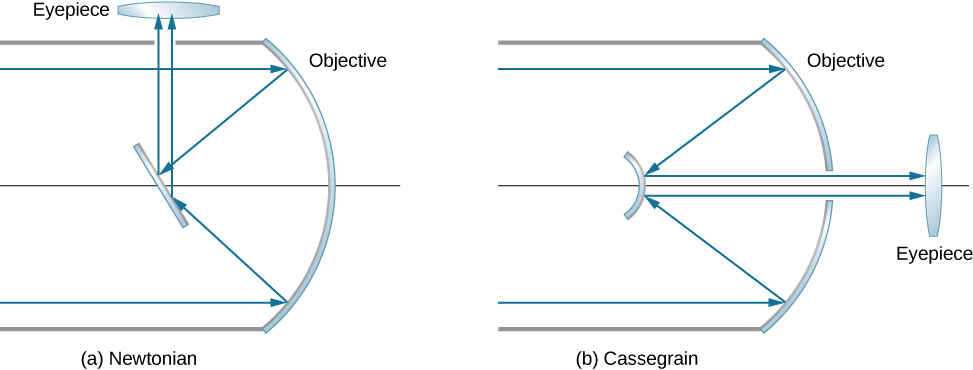
Isaac Newton designed the first reflecting telescope around 1670 to solve the problem of chromatic aberration that happens in all refracting telescopes. In chromatic aberration, light of different colors refracts by slightly different amounts in the lens. As a result, a rainbow appears around the image and the image appears blurred. In the reflecting telescope, light rays from a distant source fall upon the surface of a concave mirror fixed at the bottom end of the tube. The use of a mirror instead of a lens eliminates chromatic aberration. The concave mirror focuses the rays on its focal plane. The design problem is how to observe the focused image. Newton used a design in which the focused light from the concave mirror was reflected to one side of the tube into an eyepiece [part (a) of [link] ]. This arrangement is common in many amateur telescopes and is called the Newtonian design .
Some telescopes reflect the light back toward the middle of the concave mirror using a convex mirror. In this arrangement, the light-gathering concave mirror has a hole in the middle [part (b) of the figure]. The light then is incident on an eyepiece lens. This arrangement of the objective and eyepiece is called the Cassegrain design . Most big telescopes, including the Hubble space telescope, are of this design. Other arrangements are also possible. In some telescopes, a light detector is placed right at the spot where light is focused by the curved mirror.
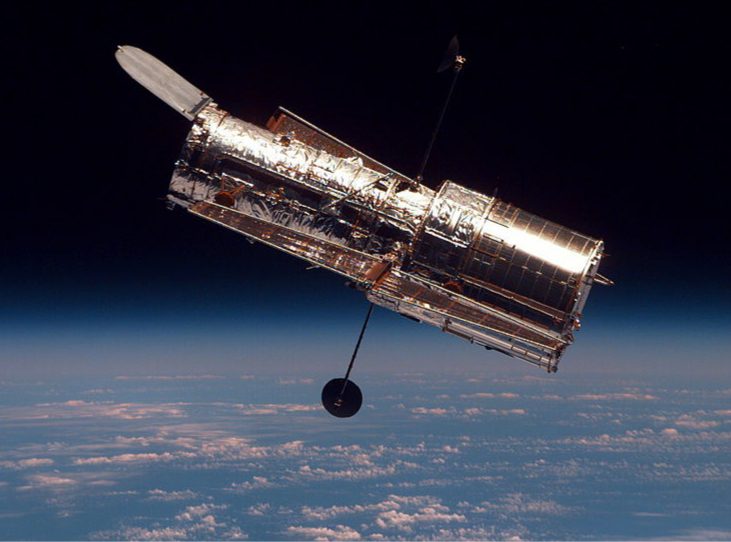
Most astronomical research telescopes are now of the reflecting type. One of the earliest large telescopes of this kind is the Hale 200-inch (or 5-meter) telescope built on Mount Palomar in southern California, which has a 200 inch-diameter mirror. One of the largest telescopes in the world is the 10-meter Keck telescope at the Keck Observatory on the summit of the dormant Mauna Kea volcano in Hawaii. The Keck Observatory operates two 10-meter telescopes. Each is not a single mirror, but is instead made up of 36 hexagonal mirrors. Furthermore, the two telescopes on the Keck can work together, which increases their power to an effective 85-meter mirror. The Hubble telescope ( [link] ) is another large reflecting telescope with a 2.4 meter-diameter primary mirror. The Hubble was put into orbit around Earth in 1990.

The angular magnification M of a reflecting telescope is also given by [link] . For a spherical mirror, the focal length is half the radius of curvature, so making a large objective mirror not only helps the telescope collect more light but also increases the magnification of the image.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?