| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we apply Schrӧdinger’s equation to a particle bound to a one-dimensional box. This special case provides lessons for understanding quantum mechanics in more complex systems. The energy of the particle is quantized as a consequence of a standing wave condition inside the box.
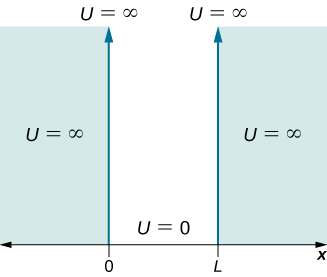
Consider a particle of mass that is allowed to move only along the x -direction and its motion is confined to the region between hard and rigid walls located at and at ( [link] ). Between the walls, the particle moves freely. This physical situation is called the infinite square well , described by the potential energy function
Combining this equation with Schrӧdinger’s time-independent wave equation gives
where E is the total energy of the particle. What types of solutions do we expect? The energy of the particle is a positive number, so if the value of the wave function is positive (right side of the equation), the curvature of the wave function is negative, or concave down (left side of the equation). Similarly, if the value of the wave function is negative (right side of the equation), the curvature of the wave function is positive or concave up (left side of equation). This condition is met by an oscillating wave function, such as a sine or cosine wave. Since these waves are confined to the box, we envision standing waves with fixed endpoints at and .
Solutions to this equation have a probabilistic interpretation. In particular, the square represents the probability density of finding the particle at a particular location x . This function must be integrated to determine the probability of finding the particle in some interval of space. We are therefore looking for a normalizable solution that satisfies the following normalization condition:
The walls are rigid and impenetrable, which means that the particle is never found beyond the wall. Mathematically, this means that the solution must vanish at the walls:
We expect oscillating solutions, so the most general solution to this equation is
where k is the wave number, and and are constants. Applying the boundary condition expressed by [link] gives
Because we have , the solution must be
If is zero, for all values of x and the normalization condition, [link] , cannot be satisfied. Assuming , [link] for then gives
We discard the solution because for this quantum number would be zero everywhere—an un-normalizable and therefore unphysical solution. Substituting [link] into [link] gives

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?