| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The forces that bind nucleons together in an atomic nucleus are much greater than those that bind an electron to an atom through electrostatic attraction. This is evident by the relative sizes of the atomic nucleus and the atom respectively). The energy required to pry a nucleon from the nucleus is therefore much larger than that required to remove (or ionize) an electron in an atom. In general, all nuclear changes involve large amounts of energy per particle undergoing the reaction. This has numerous practical applications.
According to nuclear particle experiments, the total mass of a nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons (protons and neutrons). The mass difference, or mass defect , is given by
where is the total mass of the protons, is the total mass of the neutrons, and is the mass of the nucleus. According to Einstein’s special theory of relativity, mass is a measure of the total energy of a system ( ). Thus, the total energy of a nucleus is less than the sum of the energies of its constituent nucleons. The formation of a nucleus from a system of isolated protons and neutrons is therefore an exothermic reaction—meaning that it releases energy. The energy emitted, or radiated, in this process is
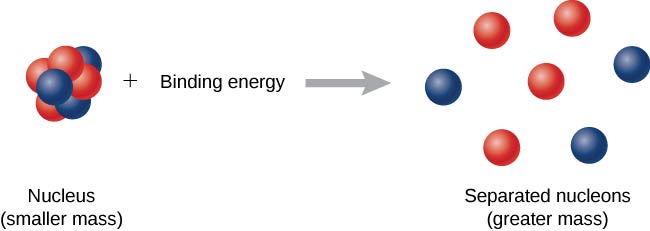
Now imagine this process occurs in reverse. Instead of forming a nucleus, energy is put into the system to break apart the nucleus ( [link] ). The amount of energy required is called the total binding energy (BE) ,
The binding energy is equal to the amount of energy released in forming the nucleus, and is therefore given by
Experimental results indicate that the binding energy for a nucleus with mass number is roughly proportional to the total number of nucleons in the nucleus, A . The binding energy of a magnesium nucleus ( ), for example, is approximately two times greater than for the carbon nucleus ( ).
The binding energy of the deuteron is then
Over two million electron volts are needed to break apart a deuteron into a proton and a neutron. This very large value indicates the great strength of the nuclear force. By comparison, the greatest amount of energy required to liberate an electron bound to a hydrogen atom by an attractive Coulomb force (an electromagnetic force) is about 10 eV.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?