| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can now determine the electric flux through an arbitrary closed surface due to an arbitrary charge distribution. We found that if a closed surface does not have any charge inside where an electric field line can terminate, then any electric field line entering the surface at one point must necessarily exit at some other point of the surface. Therefore, if a closed surface does not have any charges inside the enclosed volume, then the electric flux through the surface is zero. Now, what happens to the electric flux if there are some charges inside the enclosed volume? Gauss’s law gives a quantitative answer to this question.
To get a feel for what to expect, let’s calculate the electric flux through a spherical surface around a positive point charge q , since we already know the electric field in such a situation. Recall that when we place the point charge at the origin of a coordinate system, the electric field at a point P that is at a distance r from the charge at the origin is given by
where is the radial vector from the charge at the origin to the point P. We can use this electric field to find the flux through the spherical surface of radius r , as shown in [link] .
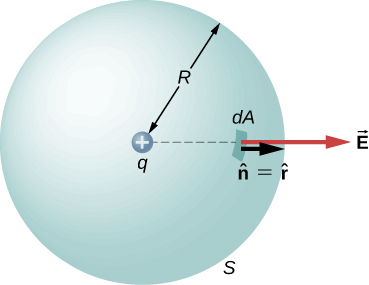
Then we apply to this system and substitute known values. On the sphere, and , so for an infinitesimal area dA ,
We now find the net flux by integrating this flux over the surface of the sphere:
where the total surface area of the spherical surface is This gives the flux through the closed spherical surface at radius r as
A remarkable fact about this equation is that the flux is independent of the size of the spherical surface. This can be directly attributed to the fact that the electric field of a point charge decreases as with distance, which just cancels the rate of increase of the surface area.
An alternative way to see why the flux through a closed spherical surface is independent of the radius of the surface is to look at the electric field lines. Note that every field line from q that pierces the surface at radius also pierces the surface at ( [link] ).
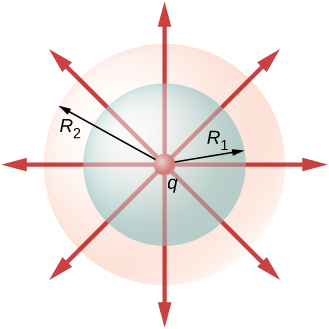
Therefore, the net number of electric field lines passing through the two surfaces from the inside to outside direction is equal. This net number of electric field lines, which is obtained by subtracting the number of lines in the direction from outside to inside from the number of lines in the direction from inside to outside gives a visual measure of the electric flux through the surfaces.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?