| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
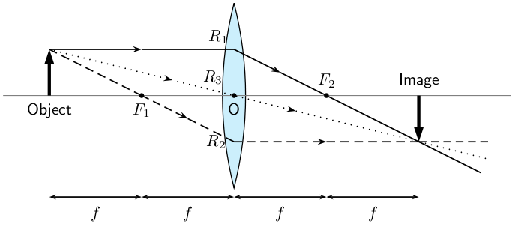
We can locate the position of the image by drawing our three rays. travels from the object to the lens parallel to the principal axis and is bent by the lens and then travels through the focal point. passes through the focal point before it enters the lens and therefore must leave the lens parallel to the principal axis. travels through the center of the lens and does not change direction. The point where , and intersect is the image of the point where they all started.
The image of an object placed at a distance equal to from the lens is upside down or inverted . This is because the rays which began at the top of the object, above the principal axis, after passing through the lens end up below the principal axis. The image is called a real image because it is on the opposite side of the lens to the object and you can trace all the light rays directly from the image back to the object.
The image is the same size as the object and is located at a distance away from the lens.
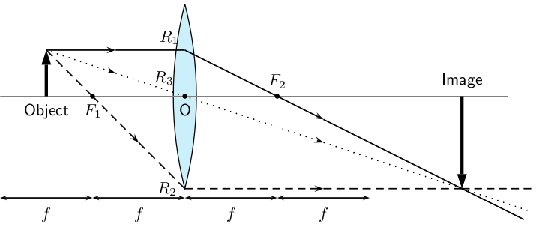
We can locate the position of the image by drawing our three rays. travels from the object to the lens parallel to the principal axis and is bent by the lens and then travels through the focal point. passes through the focal point before it enters the lens and therefore must leave the lens parallel to the principal axis. travels through the center of the lens and does not change direction. The point where , and intersect is the image of the point where they all started.
The image of an object placed at a distance between and from the lens is upside down or inverted . This is because the rays which began at the top of the object, above the principal axis, after passing through the lens end up below the principal axis. The image is called a real image because it is on the opposite side of the lens to the object and you can trace all the light rays directly from the image back to the object.
The image is larger than the object and is located at a distance greater than away from the lens.
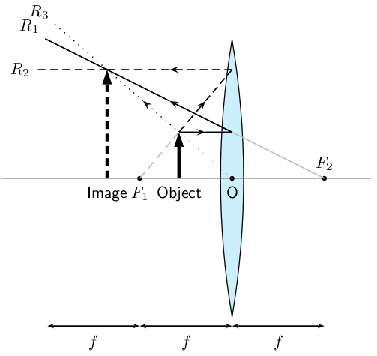
We can locate the position of the image by drawing our three rays. travels from the object to the lens parallel to the principal axis and is bent by the lens and then travels through the focal point. passes through the focal point before it enters the lens and therefore must leave the lens parallel to the principal axis. travels through the center of the lens and does not change direction. The point where , and intersect is the image of the point where they all started.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?