| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
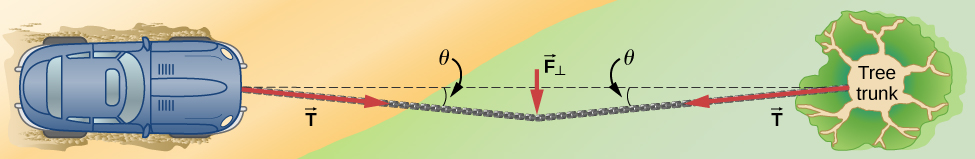
Check Your Understanding One end of a 3.0-m rope is tied to a tree; the other end is tied to a car stuck in the mud. The motorist pulls sideways on the midpoint of the rope, displacing it a distance of 0.25 m. If he exerts a force of 200.0 N under these conditions, determine the force exerted on the car.
N
In Applications of Newton’s Laws , we extend the discussion on tension in a cable to include cases in which the angles shown are not equal.
Friction is a resistive force opposing motion or its tendency. Imagine an object at rest on a horizontal surface. The net force acting on the object must be zero, leading to equality of the weight and the normal force, which act in opposite directions. If the surface is tilted, the normal force balances the component of the weight perpendicular to the surface. If the object does not slide downward, the component of the weight parallel to the inclined plane is balanced by friction. Friction is discussed in greater detail in the next chapter.
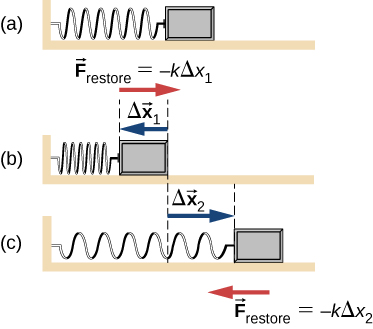
A spring is a special medium with a specific atomic structure that has the ability to restore its shape, if deformed. To restore its shape, a spring exerts a restoring force that is proportional to and in the opposite direction in which it is stretched or compressed. This is the statement of a law known as Hooke’s law, which has the mathematical form
The constant of proportionality k is a measure of the spring’s stiffness. The line of action of this force is parallel to the spring axis, and the sense of the force is in the opposite direction of the displacement vector ( [link] ). The displacement must be measured from the relaxed position; when the spring is relaxed.
There is another distinction among forces: Some forces are real, whereas others are not. Real forces have some physical origin, such as a gravitational pull. In contrast, fictitious forces arise simply because an observer is in an accelerating or noninertial frame of reference, such as one that rotates (like a merry-go-round) or undergoes linear acceleration (like a car slowing down). For example, if a satellite is heading due north above Earth’s Northern Hemisphere, then to an observer on Earth, it will appear to experience a force to the west that has no physical origin. Instead, Earth is rotating toward the east and moves east under the satellite. In Earth’s frame, this looks like a westward force on the satellite, or it can be interpreted as a violation of Newton’s first law (the law of inertia). We can identify a fictitious force by asking the question, “What is the reaction force?” If we cannot name the reaction force, then the force we are considering is fictitious. In the example of the satellite, the reaction force would have to be an eastward force on Earth. Recall that an inertial frame of reference is one in which all forces are real and, equivalently, one in which Newton’s laws have the simple forms given in this chapter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?