| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| First Equilibrium Condition | |
| Second Equilibrium Condition | |
| Linear relation between
stress and strain |
|
| Young’s modulus | |
| Bulk modulus | |
| Shear modulus |
Note: Unless stated otherwise, the weights of the wires, rods, and other elements are assumed to be negligible. Elastic moduli of selected materials are given in [link] .
What is meant when a fishing line is designated as “a 10-lb test?”
Steel rods are commonly placed in concrete before it sets. What is the purpose of these rods?
It acts as “reinforcement,” increasing a range of strain values before the structure reaches its breaking point.
A uniform rope of cross-sectional area breaks when the tensile stress in it reaches (a) What is the maximum load that can be lifted slowly at a constant speed by the rope? (b) What is the maximum load that can be lifted by the rope with an acceleration of
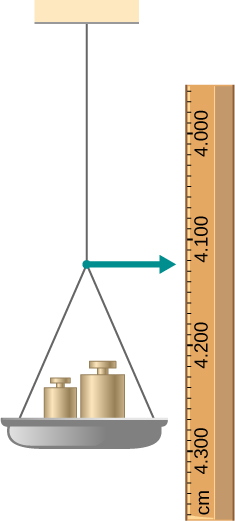
One end of a vertical metallic wire of length 2.0 m and diameter 1.0 mm is attached to a ceiling, and the other end is attached to a 5.0-N weight pan, as shown below. The position of the pointer before the pan is 4.000 cm. Different weights are then added to the pan area, and the position of the pointer is recorded in the table shown. Plot stress versus strain for this wire, then use the resulting curve to determine Young’s modulus and the proportionality limit of the metal. What metal is this most likely to be?
| Added load (including pan)
(N) |
Scale reading
(cm) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 4.000 |
| 15 | 4.036 |
| 25 | 4.073 |
| 35 | 4.109 |
| 45 | 4.146 |
| 55 | 4.181 |
| 65 | 4.221 |
| 75 | 4.266 |
| 85 | 4.316 |
An aluminum wire is suspended from the ceiling and hangs vertically. How long must the wire be before the stress at its upper end reaches the proportionality limit, which is
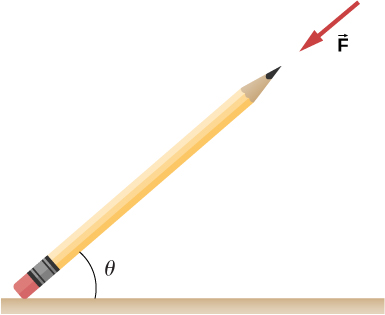
The coefficient of static friction between the rubber eraser of the pencil and the tabletop is If the force is applied along the axis of the pencil, as shown below, what is the minimum angle at which the pencil can stand without slipping? Ignore the weight of the pencil.
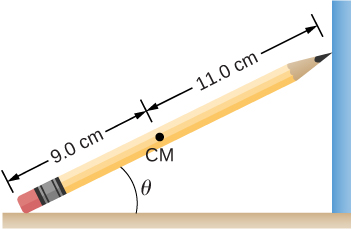
A pencil rests against a corner, as shown below. The sharpened end of the pencil touches a smooth vertical surface and the eraser end touches a rough horizontal floor. The coefficient of static friction between the eraser and the floor is The center of mass of the pencil is located 9.0 cm from the tip of the eraser and 11.0 cm from the tip of the pencil lead. Find the minimum angle for which the pencil does not slip.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?