| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Vectors are usually described in terms of their components in a coordinate system . Even in everyday life we naturally invoke the concept of orthogonal projections in a rectangular coordinate system. For example, if you ask someone for directions to a particular location, you will more likely be told to go 40 km east and 30 km north than 50 km in the direction north of east.
In a rectangular (Cartesian) xy -coordinate system in a plane, a point in a plane is described by a pair of coordinates ( x , y ). In a similar fashion, a vector in a plane is described by a pair of its vector coordinates. The x -coordinate of vector is called its x -component and the y -coordinate of vector is called its y -component. The vector x -component is a vector denoted by . The vector y -component is a vector denoted by . In the Cartesian system, the x and y vector components of a vector are the orthogonal projections of this vector onto the x - and y -axes, respectively. In this way, following the parallelogram rule for vector addition, each vector on a Cartesian plane can be expressed as the vector sum of its vector components:
As illustrated in [link] , vector is the diagonal of the rectangle where the x -component is the side parallel to the x -axis and the y -component is the side parallel to the y -axis. Vector component is orthogonal to vector component .
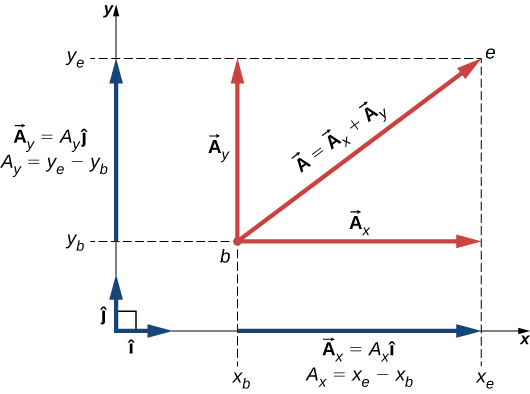
It is customary to denote the positive direction on the x -axis by the unit vector and the positive direction on the y -axis by the unit vector . Unit vectors of the axes , and , define two orthogonal directions in the plane. As shown in [link] , the x - and y - components of a vector can now be written in terms of the unit vectors of the axes:
The vectors and defined by [link] are the vector components of vector . The numbers and that define the vector components in [link] are the scalar component s of vector . Combining [link] with [link] , we obtain the component form of a vector :
If we know the coordinates of the origin point of a vector (where b stands for “beginning”) and the coordinates of the end point of a vector (where e stands for “end”), we can obtain the scalar components of a vector simply by subtracting the origin point coordinates from the end point coordinates:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?