| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
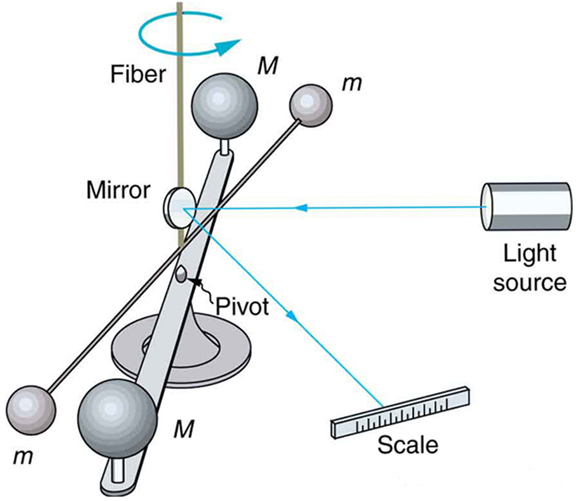
As previously noted, the universal gravitational constant is determined experimentally. This definition was first done accurately by Henry Cavendish (1731–1810), an English scientist, in 1798, more than 100 years after Newton published his universal law of gravitation. The measurement of is very basic and important because it determines the strength of one of the four forces in nature. Cavendish’s experiment was very difficult because he measured the tiny gravitational attraction between two ordinary-sized masses (tens of kilograms at most), using apparatus like that in [link] . Remarkably, his value for differs by less than 1% from the best modern value.
One important consequence of knowing was that an accurate value for Earth’s mass could finally be obtained. This was done by measuring the acceleration due to gravity as accurately as possible and then calculating the mass of Earth from the relationship Newton’s universal law of gravitation gives
where is the mass of the object, is the mass of Earth, and is the distance to the center of Earth (the distance between the centers of mass of the object and Earth). See [link] . The mass of the object cancels, leaving an equation for :
Rearranging to solve for yields
So can be calculated because all quantities on the right, including the radius of Earth , are known from direct measurements. We shall see in Satellites and Kepler's Laws: An Argument for Simplicity that knowing also allows for the determination of astronomical masses. Interestingly, of all the fundamental constants in physics, is by far the least well determined.
The Cavendish experiment is also used to explore other aspects of gravity. One of the most interesting questions is whether the gravitational force depends on substance as well as mass—for example, whether one kilogram of lead exerts the same gravitational pull as one kilogram of water. A Hungarian scientist named Roland von Eötvös pioneered this inquiry early in the 20th century. He found, with an accuracy of five parts per billion, that the gravitational force does not depend on the substance. Such experiments continue today, and have improved upon Eötvös’ measurements. Cavendish-type experiments such as those of Eric Adelberger and others at the University of Washington, have also put severe limits on the possibility of a fifth force and have verified a major prediction of general relativity—that gravitational energy contributes to rest mass. Ongoing measurements there use a torsion balance and a parallel plate (not spheres, as Cavendish used) to examine how Newton’s law of gravitation works over sub-millimeter distances. On this small-scale, do gravitational effects depart from the inverse square law? So far, no deviation has been observed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?