| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When you use a voltmeter or ammeter, you are connecting another resistor to an existing circuit and, thus, altering the circuit. Ideally, voltmeters and ammeters do not appreciably affect the circuit, but it is instructive to examine the circumstances under which they do or do not interfere.
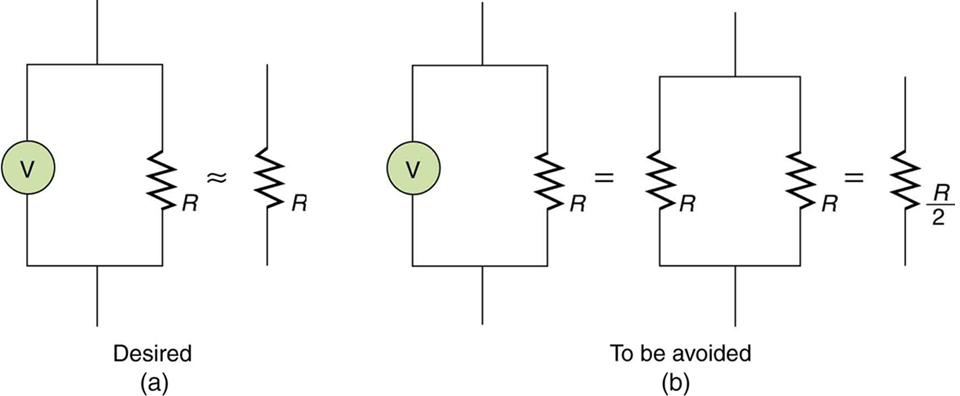
First, consider the voltmeter, which is always placed in parallel with the device being measured. Very little current flows through the voltmeter if its resistance is a few orders of magnitude greater than the device, and so the circuit is not appreciably affected. (See [link] (a).) (A large resistance in parallel with a small one has a combined resistance essentially equal to the small one.) If, however, the voltmeter’s resistance is comparable to that of the device being measured, then the two in parallel have a smaller resistance, appreciably affecting the circuit. (See [link] (b).) The voltage across the device is not the same as when the voltmeter is out of the circuit.
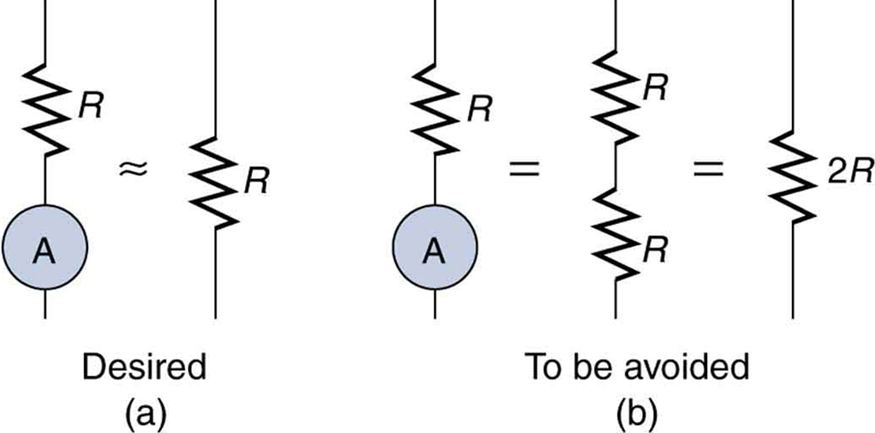
An ammeter is placed in series in the branch of the circuit being measured, so that its resistance adds to that branch. Normally, the ammeter’s resistance is very small compared with the resistances of the devices in the circuit, and so the extra resistance is negligible. (See [link] (a).) However, if very small load resistances are involved, or if the ammeter is not as low in resistance as it should be, then the total series resistance is significantly greater, and the current in the branch being measured is reduced. (See [link] (b).)
A practical problem can occur if the ammeter is connected incorrectly. If it was put in parallel with the resistor to measure the current in it, you could possibly damage the meter; the low resistance of the ammeter would allow most of the current in the circuit to go through the galvanometer, and this current would be larger since the effective resistance is smaller.
One solution to the problem of voltmeters and ammeters interfering with the circuits being measured is to use galvanometers with greater sensitivity. This allows construction of voltmeters with greater resistance and ammeters with smaller resistance than when less sensitive galvanometers are used.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?