| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
where is the -component of the angular momentum and is the angular momentum projection quantum number. The rule in parentheses for the values of is that it can range from to in steps of one. For example, if , then can have the five values –2, –1, 0, 1, and 2. Each corresponds to a different energy in the presence of a magnetic field, so that they are related to the splitting of spectral lines into discrete parts, as discussed in the preceding section. If the -component of angular momentum can have only certain values, then the angular momentum can have only certain directions, as illustrated in [link] .
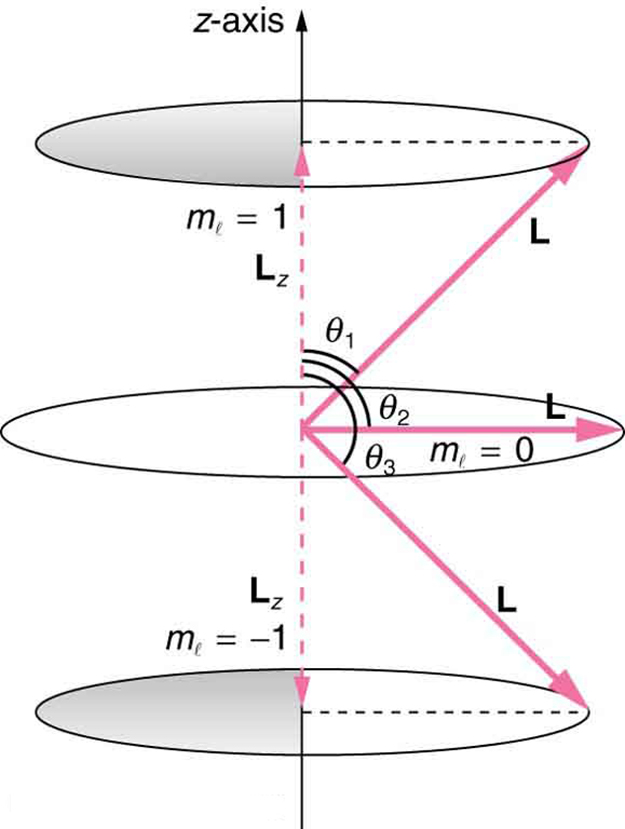
Calculate the angles that the angular momentum vector can make with the -axis for , as illustrated in [link] .
Strategy
[link] represents the vectors and as usual, with arrows proportional to their magnitudes and pointing in the correct directions. and form a right triangle, with being the hypotenuse and the adjacent side. This means that the ratio of to is the cosine of the angle of interest. We can find and using and .
Solution
We are given , so that can be +1, 0, or −1. Thus has the value given by .
can have three values, given by .
As can be seen in [link] , and so for , we have
Thus,
Similarly, for , we find ; thus,
And for ,
so that
Discussion
The angles are consistent with the figure. Only the angle relative to the -axis is quantized. can point in any direction as long as it makes the proper angle with the -axis. Thus the angular momentum vectors lie on cones as illustrated. This behavior is not observed on the large scale. To see how the correspondence principle holds here, consider that the smallest angle ( in the example) is for the maximum value of , namely . For that smallest angle,
which approaches 1 as becomes very large. If , then . Furthermore, for large , there are many values of , so that all angles become possible as gets very large.
There are two more quantum numbers of immediate concern. Both were first discovered for electrons in conjunction with fine structure in atomic spectra. It is now well established that electrons and other fundamental particles have intrinsic spin , roughly analogous to a planet spinning on its axis. This spin is a fundamental characteristic of particles, and only one magnitude of intrinsic spin is allowed for a given type of particle. Intrinsic angular momentum is quantized independently of orbital angular momentum. Additionally, the direction of the spin is also quantized. It has been found that the magnitude of the intrinsic (internal) spin angular momentum , , of an electron is given by

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?