| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
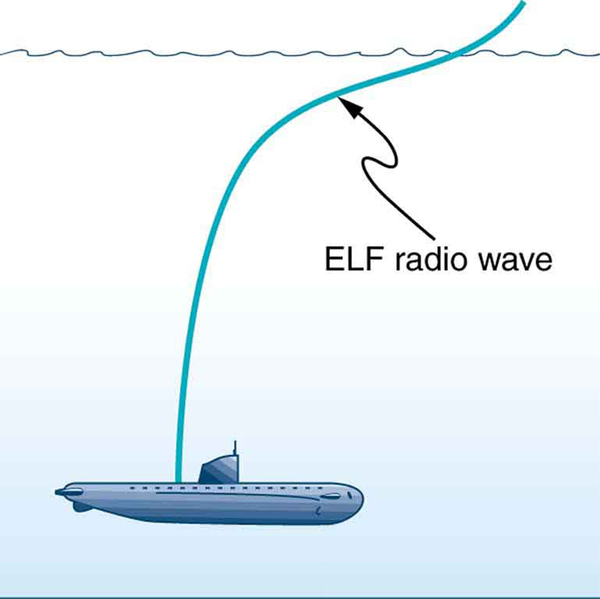
Extremely low frequency (ELF) radio waves of about 1 kHz are used to communicate with submerged submarines. The ability of radio waves to penetrate salt water is related to their wavelength (much like ultrasound penetrating tissue)—the longer the wavelength, the farther they penetrate. Since salt water is a good conductor, radio waves are strongly absorbed by it, and very long wavelengths are needed to reach a submarine under the surface. (See [link] .)
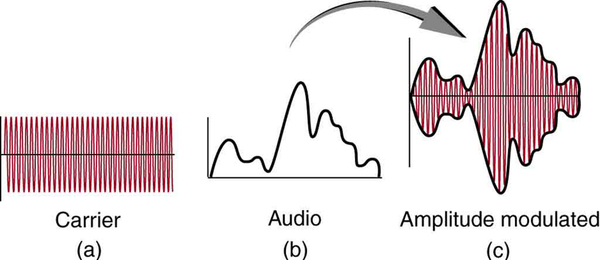
AM radio waves are used to carry commercial radio signals in the frequency range from 540 to 1600 kHz. The abbreviation AM stands for amplitude modulation , which is the method for placing information on these waves. (See [link] .) A carrier wave having the basic frequency of the radio station, say 1530 kHz, is varied or modulated in amplitude by an audio signal. The resulting wave has a constant frequency, but a varying amplitude.
A radio receiver tuned to have the same resonant frequency as the carrier wave can pick up the signal, while rejecting the many other frequencies impinging on its antenna. The receiver’s circuitry is designed to respond to variations in amplitude of the carrier wave to replicate the original audio signal. That audio signal is amplified to drive a speaker or perhaps to be recorded.
FM radio waves are also used for commercial radio transmission, but in the frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz. FM stands for frequency modulation , another method of carrying information. (See [link] .) Here a carrier wave having the basic frequency of the radio station, perhaps 105.1 MHz, is modulated in frequency by the audio signal, producing a wave of constant amplitude but varying frequency.
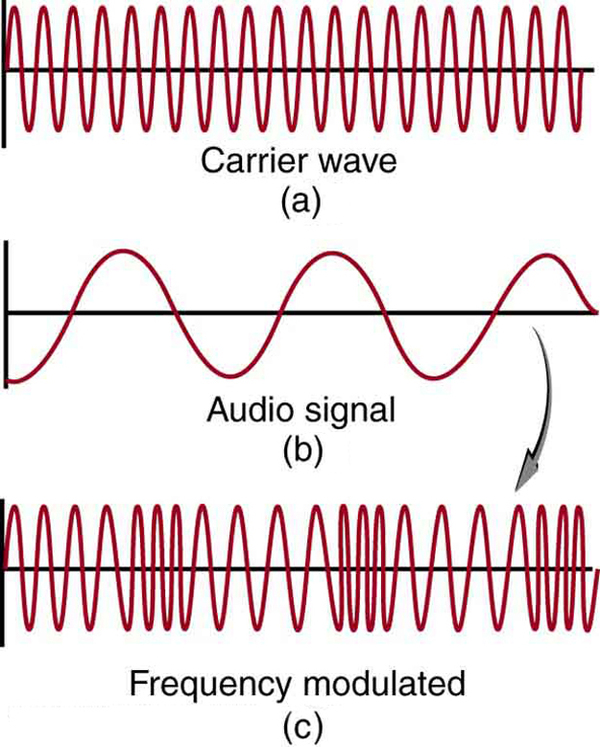
Since audible frequencies range up to 20 kHz (or 0.020 MHz) at most, the frequency of the FM radio wave can vary from the carrier by as much as 0.020 MHz. Thus the carrier frequencies of two different radio stations cannot be closer than 0.020 MHz. An FM receiver is tuned to resonate at the carrier frequency and has circuitry that responds to variations in frequency, reproducing the audio information.
FM radio is inherently less subject to noise from stray radio sources than AM radio. The reason is that amplitudes of waves add. So an AM receiver would interpret noise added onto the amplitude of its carrier wave as part of the information. An FM receiver can be made to reject amplitudes other than that of the basic carrier wave and only look for variations in frequency. It is thus easier to reject noise from FM, since noise produces a variation in amplitude.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?