| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Angular quantities like angular displacement, velocity, acceleration and torque etc. have been discussed in earlier modules. We were, however, restricted in interpreting and applying these quantities to circular motion or pure rotational motion. Essentially, these physical quantities have been visualized in reference to an axis of rotation and a circular path.
In this module, we shall expand the meaning and application of angular quantities in very general terms, capable of representing pure as well as impure rotation and translation. We shall find, in this module, that pure translation and rotation are, as a matter of fact, special cases.
Here, we shall define and interpret angular quantities very generally with respect to a "point" in the reference system - rather than an axis. This change in reference of measurement allows us to extend application of angular quantities beyond the context of rotational motion. We can actually associate all angular quantities even with a straight line motion i.e. pure translational motion. For example, we can calculate torque on a particle, which is moving along a straight line. Similarly, we can determine angular displacement and velocity for a projectile motion, which we have studied strictly from the point of view of translation. We shall work out appropriate examples to illustrate extension of angular concepts to these motions.
We must understand here that the broadening the concept of angular quantities is not without purpose. We shall find out in the subsequent modules that the de-linking of angular concepts like torque and angular momentum from an axis, lets us derive very powerful law known as conservation of angular momentum.
The example given below calculates average angular velocity of a projectile to highlight the generality of angular quantity.
Problem 1 : A particle is projected with velocity "v" at an angle of "θ" with the horizontal. Find the average angular speed of the particle between point of projection and point of impact.
Solution : The average angular speed is given by :
Angular velocity
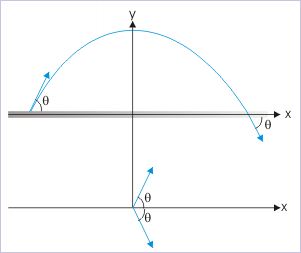
From the figure, magnitude of the total angular displacement is :
On the other hand, time of flight is given by :
Putting these values in the expression of angular velocity, we have :
From this example, we see that we can indeed associate angular quantity like angular speed with motion like that of projectile, which is not strictly rotational.
As a particle moves, the line joining a fixed point and particle, moves through angular displacement. Important thing to note here is that the particle may not follow a circular path - it can describe any curve even a straight line. We, then, define average angular velocity as :

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?