| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Flash photography is generally not allowed of precious artworks and colored prints because the UV radiation from the flash can cause photo-degradation in the artworks. Often artworks will have an extra-thick layer of glass in front of them, which is especially designed to absorb UV radiation.
If all of the Sun’s ultraviolet radiation reached the Earth’s surface, there would be extremely grave effects on the biosphere from the severe cell damage it causes. However, the layer of ozone ( ) in our upper atmosphere (10 to 50 km above the Earth) protects life by absorbing most of the dangerous UV radiation.
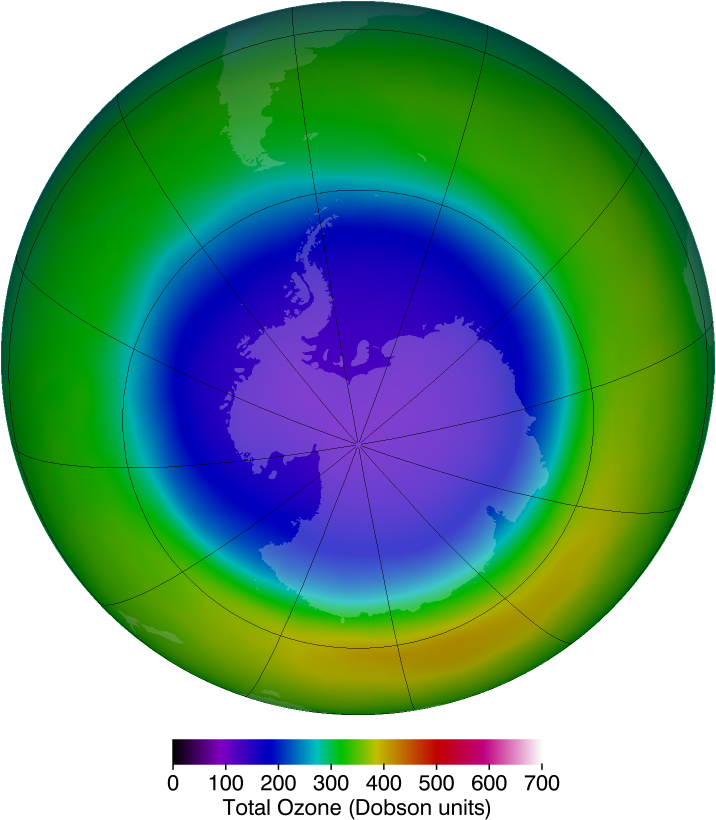
Unfortunately, today we are observing a depletion in ozone concentrations in the upper atmosphere. This depletion has led to the formation of an “ozone hole” in the upper atmosphere. The hole is more centered over the southern hemisphere, and changes with the seasons, being largest in the spring. This depletion is attributed to the breakdown of ozone molecules by refrigerant gases called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
The UV radiation helps dissociate the CFC’s, releasing highly reactive chlorine (Cl) atoms, which catalyze the destruction of the ozone layer. For example, the reaction of with a photon of light can be written as:
The Cl atom then catalyzes the breakdown of ozone as follows:
A single chlorine atom could destroy ozone molecules for up to two years before being transported down to the surface. The CFCs are relatively stable and will contribute to ozone depletion for years to come. CFCs are found in refrigerants, air conditioning systems, foams, and aerosols.
International concern over this problem led to the establishment of the “Montreal Protocol” agreement (1987) to phase out CFC production in most countries. However, developing-country participation is needed if worldwide production and elimination of CFCs is to be achieved. Probably the largest contributor to CFC emissions today is India. But the protocol seems to be working, as there are signs of an ozone recovery. (See [link] .)
Besides the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation, there are also benefits of exposure in nature and uses in technology. Vitamin D production in the skin (epidermis) results from exposure to UVB radiation, generally from sunlight. A number of studies indicate lack of vitamin D can result in the development of a range of cancers (prostate, breast, colon), so a certain amount of UV exposure is helpful. Lack of vitamin D is also linked to osteoporosis. Exposures (with no sunscreen) of 10 minutes a day to arms, face, and legs might be sufficient to provide the accepted dietary level. However, in the winter time north of about latitude, most UVB gets blocked by the atmosphere.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?