| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The second postulate of relativity (verified by extensive experimental observation) says that classical velocity addition does not apply to light. Imagine a car traveling at night along a straight road, as in [link] . If classical velocity addition applied to light, then the light from the car’s headlights would approach the observer on the sidewalk at a speed . But we know that light will move away from the car at speed relative to the driver of the car, and light will move towards the observer on the sidewalk at speed , too.
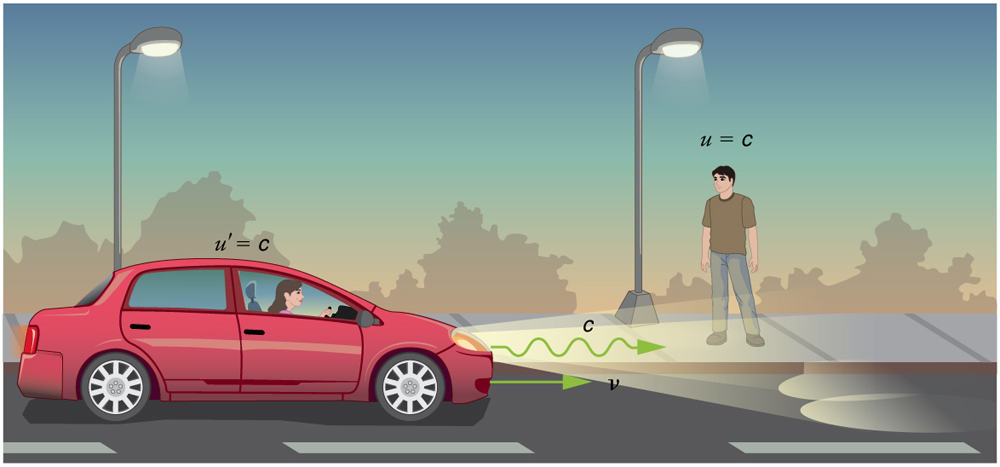

Either light is an exception, or the classical velocity addition formula only works at low velocities. The latter is the case. The correct formula for one-dimensional relativistic velocity addition is
where is the relative velocity between two observers, is the velocity of an object relative to one observer, and is the velocity relative to the other observer. (For ease of visualization, we often choose to measure in our reference frame, while someone moving at relative to us measures .) Note that the term becomes very small at low velocities, and gives a result very close to classical velocity addition. As before, we see that classical velocity addition is an excellent approximation to the correct relativistic formula for small velocities. No wonder that it seems correct in our experience.
Suppose a spaceship heading directly towards the Earth at half the speed of light sends a signal to us on a laser-produced beam of light. Given that the light leaves the ship at speed as observed from the ship, calculate the speed at which it approaches the Earth.
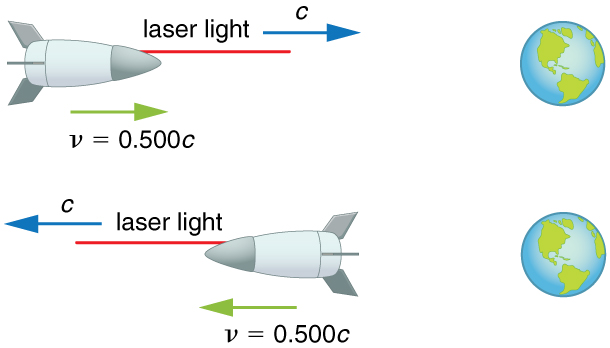
Strategy
Because the light and the spaceship are moving at relativistic speeds, we cannot use simple velocity addition. Instead, we can determine the speed at which the light approaches the Earth using relativistic velocity addition.
Solution
Discussion
Relativistic velocity addition gives the correct result. Light leaves the ship at speed and approaches the Earth at speed . The speed of light is independent of the relative motion of source and observer, whether the observer is on the ship or Earth-bound.
Velocities cannot add to greater than the speed of light, provided that is less than and does not exceed . The following example illustrates that relativistic velocity addition is not as symmetric as classical velocity addition.
Suppose the spaceship in the previous example is approaching the Earth at half the speed of light and shoots a canister at a speed of . (a) At what velocity will an Earth-bound observer see the canister if it is shot directly towards the Earth? (b) If it is shot directly away from the Earth? (See [link] .)
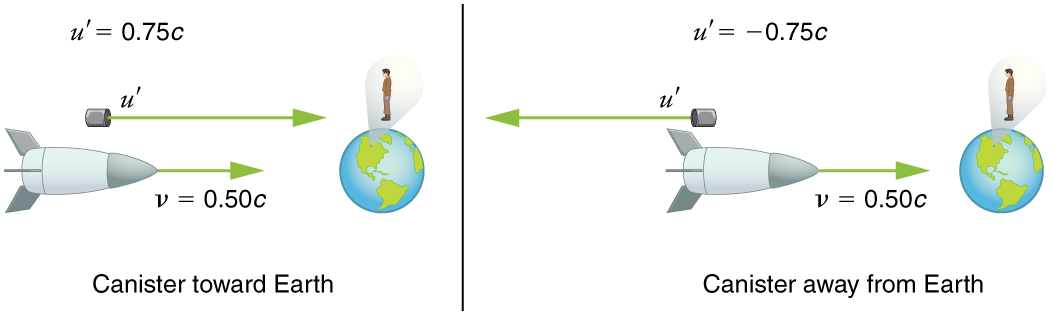
Strategy
Because the canister and the spaceship are moving at relativistic speeds, we must determine the speed of the canister by an Earth-bound observer using relativistic velocity addition instead of simple velocity addition.
Solution for (a)
Solution for (b)
Discussion
The minus sign indicates velocity away from the Earth (in the opposite direction from ), which means the canister is heading towards the Earth in part (a) and away in part (b), as expected. But relativistic velocities do not add as simply as they do classically. In part (a), the canister does approach the Earth faster, but not at the simple sum of . The total velocity is less than you would get classically. And in part (b), the canister moves away from the Earth at a velocity of , which is faster than the you would expect classically. The velocities are not even symmetric. In part (a) the canister moves faster than the ship relative to the Earth, whereas in part (b) it moves slower than the ship.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?