| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
where is torque, is the distance from the pivot point to the point where the force is applied, is the magnitude of the force, and is the angle between and the vector directed from the point where the force acts to the pivot point. The perpendicular lever arm is defined to be
so that
By convention, counterclockwise torques are positive, and clockwise torques are negative.
What three factors affect the torque created by a force relative to a specific pivot point?
A wrecking ball is being used to knock down a building. One tall unsupported concrete wall remains standing. If the wrecking ball hits the wall near the top, is the wall more likely to fall over by rotating at its base or by falling straight down? Explain your answer. How is it most likely to fall if it is struck with the same force at its base? Note that this depends on how firmly the wall is attached at its base.
Mechanics sometimes put a length of pipe over the handle of a wrench when trying to remove a very tight bolt. How does this help? (It is also hazardous since it can break the bolt.)
(a) When opening a door, you push on it perpendicularly with a force of 55.0 N at a distance of 0.850m from the hinges. What torque are you exerting relative to the hinges? (b) Does it matter if you push at the same height as the hinges?
a)
b) It does not matter at what height you push. The torque depends on only the magnitude of the force applied and the perpendicular distance of the force's application from the hinges. (Children don't have a tougher time opening a door because they push lower than adults, they have a tougher time because they don't push far enough from the hinges.)
When tightening a bolt, you push perpendicularly on a wrench with a force of 165 N at a distance of 0.140 m from the center of the bolt. (a) How much torque are you exerting in newton × meters (relative to the center of the bolt)? (b) Convert this torque to footpounds.
Two children push on opposite sides of a door during play. Both push horizontally and perpendicular to the door. One child pushes with a force of 17.5 N at a distance of 0.600 m from the hinges, and the second child pushes at a distance of 0.450 m. What force must the second child exert to keep the door from moving? Assume friction is negligible.
23.3 N
Use the second condition for equilibrium to calculate in [link] , employing any data given or solved for in part (a) of the example.
Repeat the seesaw problem in [link] with the center of mass of the seesaw 0.160 m to the left of the pivot (on the side of the lighter child) and assuming a mass of 12.0 kg for the seesaw. The other data given in the example remain unchanged. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for static equilibrium.
Given:
a) Since children are balancing:
So, solving for gives:
b) Since the children are not moving:
So that
Which of the following is not an example of an object undergoing a torque?
(a)
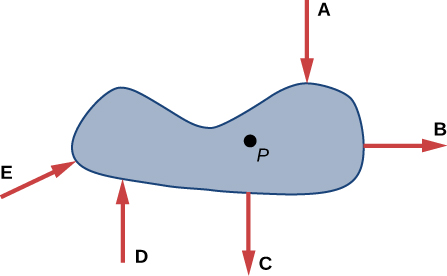
Five forces of equal magnitude, labeled A – E , are applied to the object shown below. If the object is anchored at point P , which force will provide the greatest torque?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?