| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
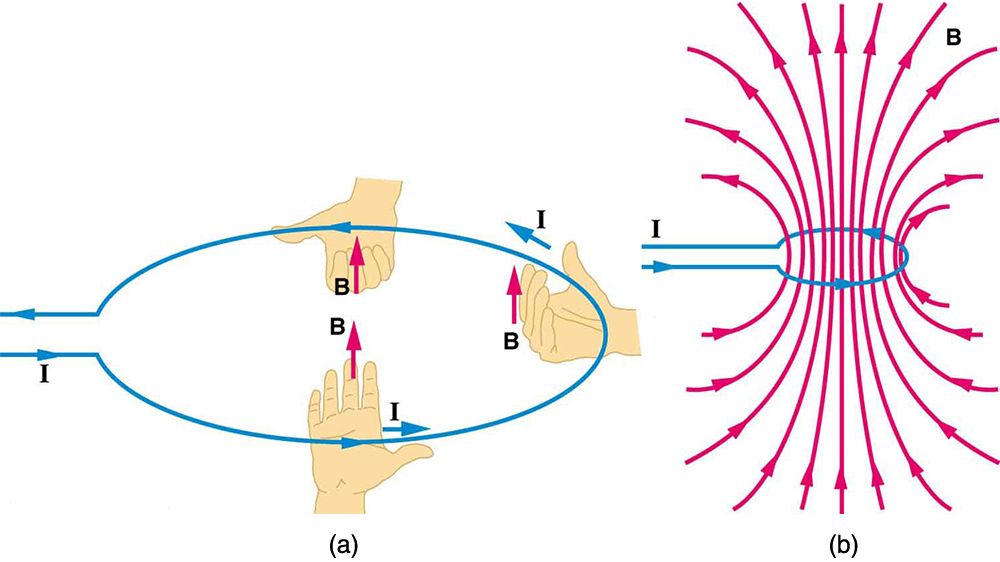
The magnetic field near a current-carrying loop of wire is shown in [link] . Both the direction and the magnitude of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying loop are complex. RHR-2 can be used to give the direction of the field near the loop, but mapping with compasses and the rules about field lines given in Magnetic Fields and Magnetic Field Lines are needed for more detail. There is a simple formula for the magnetic field strength at the center of a circular loop . It is
where is the radius of the loop. This equation is very similar to that for a straight wire, but it is valid only at the center of a circular loop of wire. The similarity of the equations does indicate that similar field strength can be obtained at the center of a loop. One way to get a larger field is to have loops; then, the field is . Note that the larger the loop, the smaller the field at its center, because the current is farther away.
A solenoid is a long coil of wire (with many turns or loops, as opposed to a flat loop). Because of its shape, the field inside a solenoid can be very uniform, and also very strong. The field just outside the coils is nearly zero. [link] shows how the field looks and how its direction is given by RHR-2.
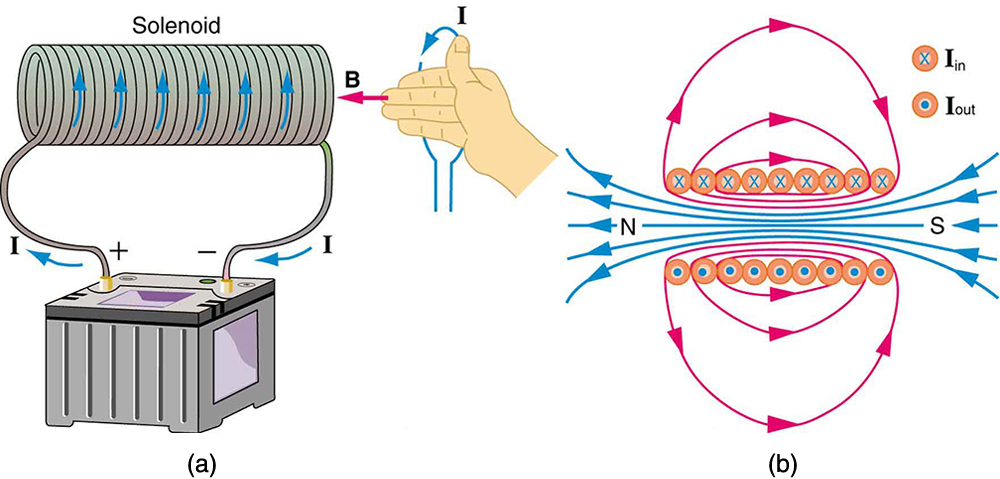
The magnetic field inside of a current-carrying solenoid is very uniform in direction and magnitude. Only near the ends does it begin to weaken and change direction. The field outside has similar complexities to flat loops and bar magnets, but the magnetic field strength inside a solenoid is simply
where is the number of loops per unit length of the solenoid , with being the number of loops and the length). Note that is the field strength anywhere in the uniform region of the interior and not just at the center. Large uniform fields spread over a large volume are possible with solenoids, as [link] implies.
What is the field inside a 2.00-m-long solenoid that has 2000 loops and carries a 1600-A current?
Strategy
To find the field strength inside a solenoid, we use . First, we note the number of loops per unit length is
Solution
Substituting known values gives
Discussion
This is a large field strength that could be established over a large-diameter solenoid, such as in medical uses of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The very large current is an indication that the fields of this strength are not easily achieved, however. Such a large current through 1000 loops squeezed into a meter’s length would produce significant heating. Higher currents can be achieved by using superconducting wires, although this is expensive. There is an upper limit to the current, since the superconducting state is disrupted by very large magnetic fields.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?