| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
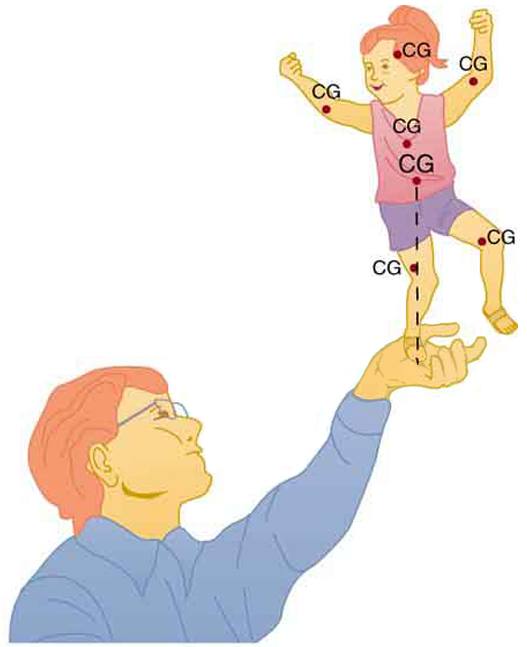
It is one thing to have a system in equilibrium; it is quite another for it to be stable. The toy doll perched on the man's hand in [link] , for example, is not in stable equilibrium. There are three types of equilibrium : stable , unstable , and neutral . Figures throughout this module illustrate various examples.
[link] presents a balanced system, such as the toy doll on the man's hand, which has its center of gravity (cg) directly over the pivot, so that the torque of the total weight is zero. This is equivalent to having the torques of the individual parts balanced about the pivot point, in this case the hand. The cgs of the arms, legs, head, and torso are labeled with smaller type.
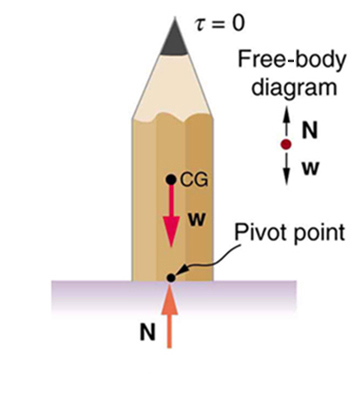
A system is said to be in stable equilibrium if, when displaced from equilibrium, it experiences a net force or torque in a direction opposite to the direction of the displacement. For example, a marble at the bottom of a bowl will experience a restoring force when displaced from its equilibrium position. This force moves it back toward the equilibrium position. Most systems are in stable equilibrium, especially for small displacements. For another example of stable equilibrium, see the pencil in [link] .
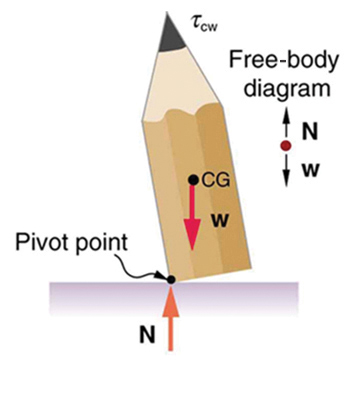
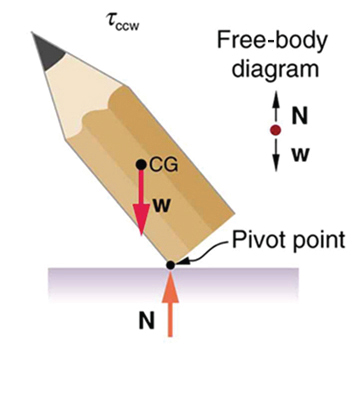
A system is in unstable equilibrium if, when displaced, it experiences a net force or torque in the same direction as the displacement from equilibrium. A system in unstable equilibrium accelerates away from its equilibrium position if displaced even slightly. An obvious example is a ball resting on top of a hill. Once displaced, it accelerates away from the crest. See the next several figures for examples of unstable equilibrium.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?