| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
In the previous section, we explored the relationship between voltage and energy. In this section, we will explore the relationship between voltage and electric field. For example, a uniform electric field is produced by placing a potential difference (or voltage) across two parallel metal plates, labeled A and B. (See [link] .) Examining this will tell us what voltage is needed to produce a certain electric field strength; it will also reveal a more fundamental relationship between electric potential and electric field. From a physicist’s point of view, either or can be used to describe any charge distribution. is most closely tied to energy, whereas is most closely related to force. is a scalar quantity and has no direction, while is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction. (Note that the magnitude of the electric field strength, a scalar quantity, is represented by below.) The relationship between and is revealed by calculating the work done by the force in moving a charge from point A to point B. But, as noted in Electric Potential Energy: Potential Difference , this is complex for arbitrary charge distributions, requiring calculus. We therefore look at a uniform electric field as an interesting special case.
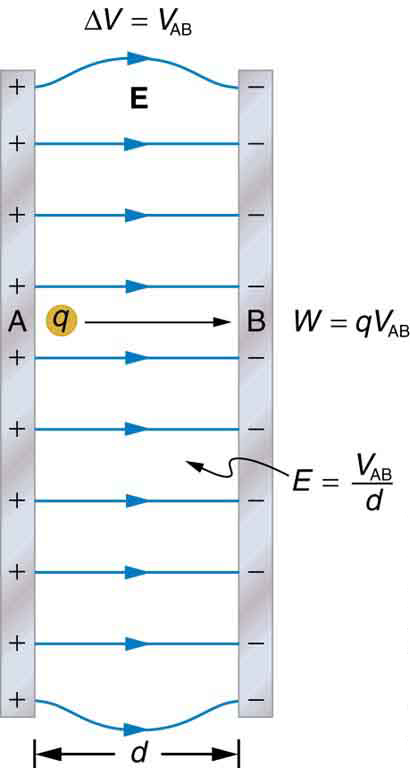
The work done by the electric field in [link] to move a positive charge from A, the positive plate, higher potential, to B, the negative plate, lower potential, is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?