| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science pracitces:
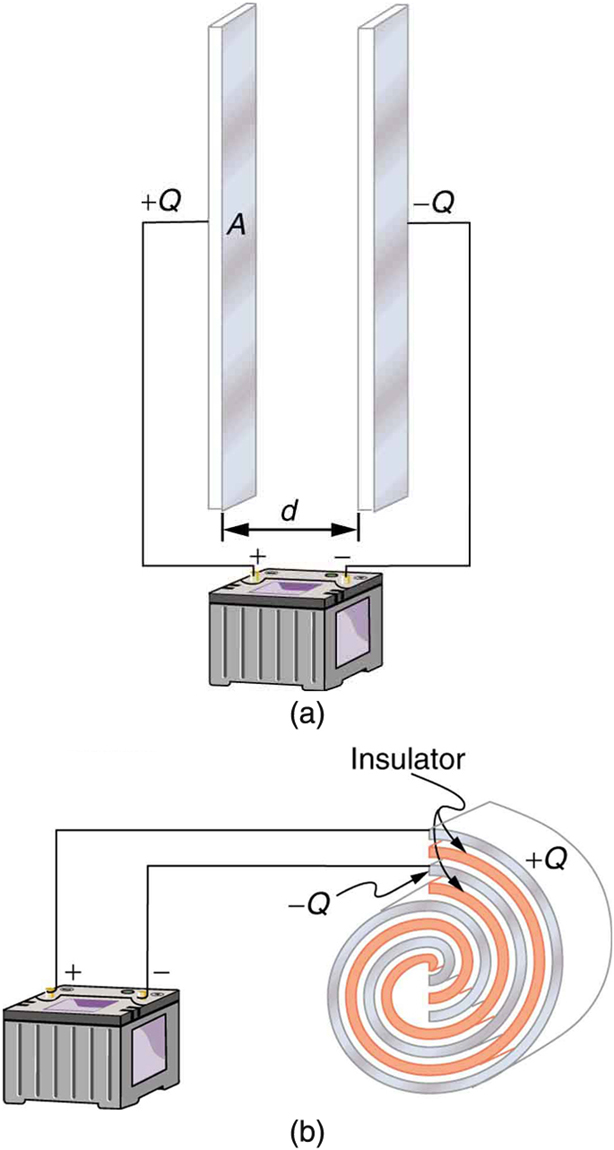
A capacitor is a device used to store electric charge. Capacitors have applications ranging from filtering static out of radio reception to energy storage in heart defibrillators. Typically, commercial capacitors have two conducting parts close to one another, but not touching, such as those in [link] . (Most of the time an insulator is used between the two plates to provide separation—see the discussion on dielectrics below.) When battery terminals are connected to an initially uncharged capacitor, equal amounts of positive and negative charge, and , are separated into its two plates. The capacitor remains neutral overall, but we refer to it as storing a charge in this circumstance.
A capacitor is a device used to store electric charge.
The amount of charge a capacitor can store depends on two major factors—the voltage applied and the capacitor’s physical characteristics, such as its size.
The amount of charge a capacitor can store depends on two major factors—the voltage applied and the capacitor’s physical characteristics, such as its size.
A system composed of two identical, parallel conducting plates separated by a distance, as in [link] , is called a parallel plate capacitor . It is easy to see the relationship between the voltage and the stored charge for a parallel plate capacitor, as shown in [link] . Each electric field line starts on an individual positive charge and ends on a negative one, so that there will be more field lines if there is more charge. (Drawing a single field line per charge is a convenience, only. We can draw many field lines for each charge, but the total number is proportional to the number of charges.) The electric field strength is, thus, directly proportional to .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?