| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
So far we have considered excess charges on a smooth, symmetrical conductor surface. What happens if a conductor has sharp corners or is pointed? Excess charges on a nonuniform conductor become concentrated at the sharpest points. Additionally, excess charge may move on or off the conductor at the sharpest points.
To see how and why this happens, consider the charged conductor in [link] . The electrostatic repulsion of like charges is most effective in moving them apart on the flattest surface, and so they become least concentrated there. This is because the forces between identical pairs of charges at either end of the conductor are identical, but the components of the forces parallel to the surfaces are different. The component parallel to the surface is greatest on the flattest surface and, hence, more effective in moving the charge.
The same effect is produced on a conductor by an externally applied electric field, as seen in [link] (c). Since the field lines must be perpendicular to the surface, more of them are concentrated on the most curved parts.
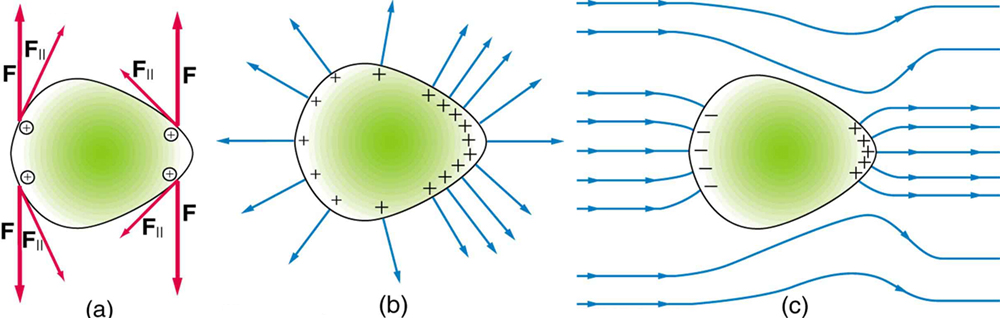
On a very sharply curved surface, such as shown in [link] , the charges are so concentrated at the point that the resulting electric field can be great enough to remove them from the surface. This can be useful.
Lightning rods work best when they are most pointed. The large charges created in storm clouds induce an opposite charge on a building that can result in a lightning bolt hitting the building. The induced charge is bled away continually by a lightning rod, preventing the more dramatic lightning strike.
Of course, we sometimes wish to prevent the transfer of charge rather than to facilitate it. In that case, the conductor should be very smooth and have as large a radius of curvature as possible. (See [link] .) Smooth surfaces are used on high-voltage transmission lines, for example, to avoid leakage of charge into the air.
Another device that makes use of some of these principles is a Faraday cage . This is a metal shield that encloses a volume. All electrical charges will reside on the outside surface of this shield, and there will be no electrical field inside. A Faraday cage is used to prohibit stray electrical fields in the environment from interfering with sensitive measurements, such as the electrical signals inside a nerve cell.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?