| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The fantastic growth in the odds favoring disorder that we see in going from 5 to 100 coins continues as the number of entities in the system increases. Let us now imagine applying this approach to perhaps a small sample of gas. Because counting microstates and macrostates involves statistics, this is called statistical analysis . The macrostates of a gas correspond to its macroscopic properties, such as volume, temperature, and pressure; and its microstates correspond to the detailed description of the positions and velocities of its atoms. Even a small amount of gas has a huge number of atoms: of an ideal gas at 1.0 atm and has atoms. So each macrostate has an immense number of microstates. In plain language, this means that there are an immense number of ways in which the atoms in a gas can be arranged, while still having the same pressure, temperature, and so on.
The most likely conditions (or macrostates) for a gas are those we see all the time—a random distribution of atoms in space with a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds in random directions, as predicted by kinetic theory. This is the most disorderly and least structured condition we can imagine. In contrast, one type of very orderly and structured macrostate has all of the atoms in one corner of a container with identical velocities. There are very few ways to accomplish this (very few microstates corresponding to it), and so it is exceedingly unlikely ever to occur. (See [link] (b).) Indeed, it is so unlikely that we have a law saying that it is impossible, which has never been observed to be violated—the second law of thermodynamics.
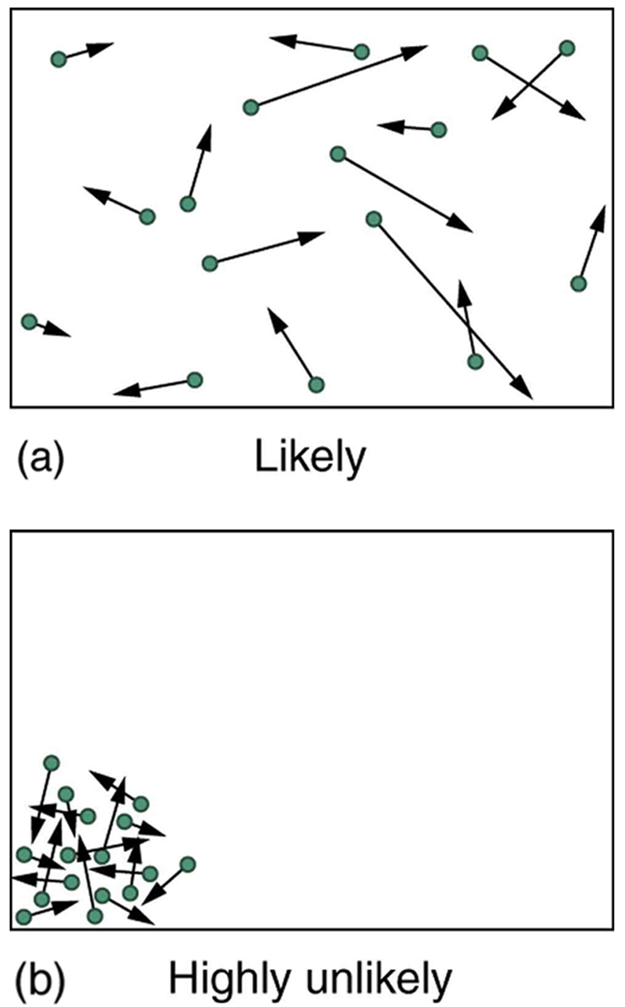
The disordered condition is one of high entropy, and the ordered one has low entropy. With a transfer of energy from another system, we could force all of the atoms into one corner and have a local decrease in entropy, but at the cost of an overall increase in entropy of the universe. If the atoms start out in one corner, they will quickly disperse and become uniformly distributed and will never return to the orderly original state ( [link] (b)). Entropy will increase. With such a large sample of atoms, it is possible—but unimaginably unlikely—for entropy to decrease. Disorder is vastly more likely than order.
The arguments that disorder and high entropy are the most probable states are quite convincing. The great Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann (1844–1906)—who, along with Maxwell, made so many contributions to kinetic theory—proved that the entropy of a system in a given state (a macrostate) can be written as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?