| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Some of the most basic characteristics of static electricity include:
How do we know there are two types of electric charge ? When various materials are rubbed together in controlled ways, certain combinations of materials always produce one type of charge on one material and the opposite type on the other. By convention, we call one type of charge “positive”, and the other type “negative.” For example, when glass is rubbed with silk, the glass becomes positively charged and the silk negatively charged. Since the glass and silk have opposite charges, they attract one another like clothes that have rubbed together in a dryer. Two glass rods rubbed with silk in this manner will repel one another, since each rod has positive charge on it. Similarly, two silk cloths so rubbed will repel, since both cloths have negative charge. [link] shows how these simple materials can be used to explore the nature of the force between charges.
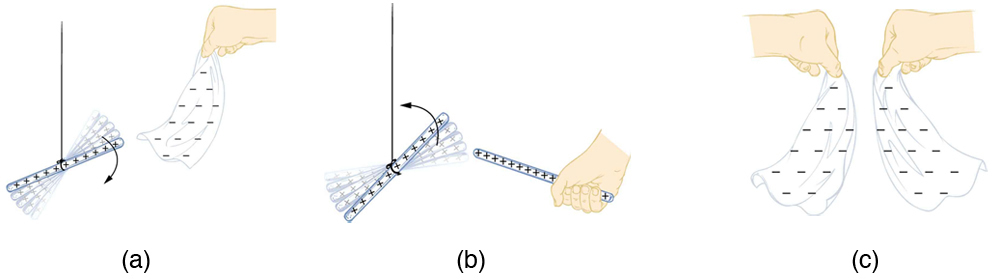
More sophisticated questions arise. Where do these charges come from? Can you create or destroy charge? Is there a smallest unit of charge? Exactly how does the force depend on the amount of charge and the distance between charges? Such questions obviously occurred to Benjamin Franklin and other early researchers, and they interest us even today.
Franklin wrote in his letters and books that he could see the effects of electric charge but did not understand what caused the phenomenon. Today we have the advantage of knowing that normal matter is made of atoms, and that atoms contain positive and negative charges, usually in equal amounts.
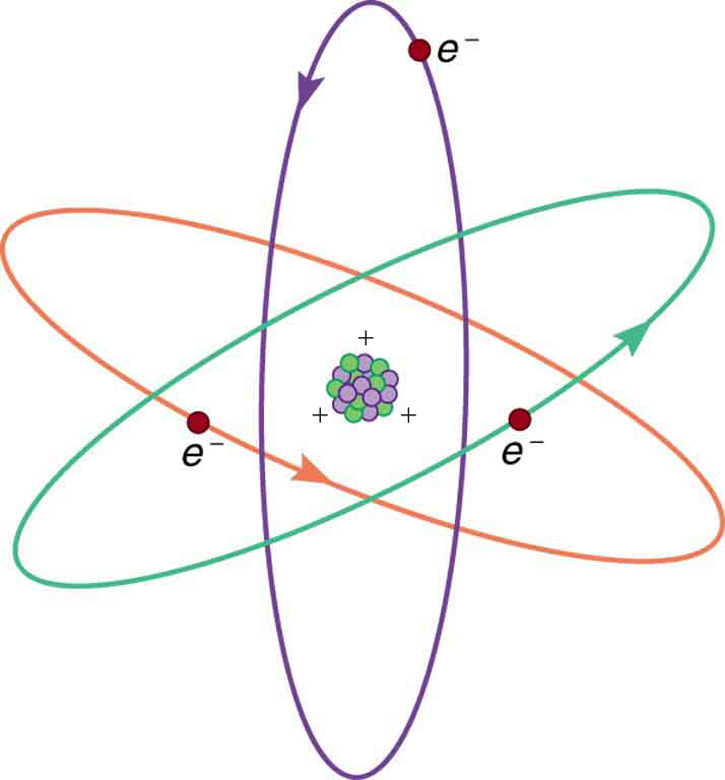
[link] shows a simple model of an atom with negative electrons orbiting its positive nucleus. The nucleus is positive due to the presence of positively charged protons . Nearly all charge in nature is due to electrons and protons, which are two of the three building blocks of most matter. (The third is the neutron, which is neutral, carrying no charge.) Other charge-carrying particles are observed in cosmic rays and nuclear decay, and are created in particle accelerators. All but the electron and proton survive only a short time and are quite rare by comparison.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?