| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An inelastic collision is one in which the internal kinetic energy changes (it is not conserved).
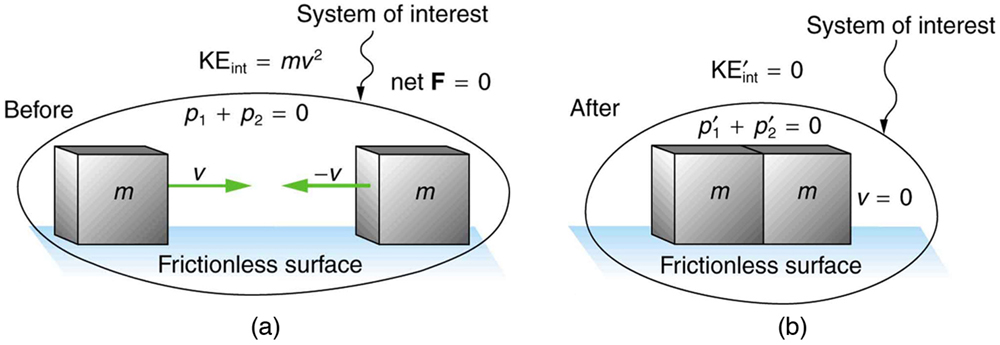
[link] shows an example of an inelastic collision. Two objects that have equal masses head toward one another at equal speeds and then stick together. Their total internal kinetic energy is initially . The two objects come to rest after sticking together, conserving momentum. But the internal kinetic energy is zero after the collision. A collision in which the objects stick together is sometimes called a perfectly inelastic collision because it reduces internal kinetic energy more than does any other type of inelastic collision. In fact, such a collision reduces internal kinetic energy to the minimum it can have while still conserving momentum.
A collision in which the objects stick together is sometimes called “perfectly inelastic.”
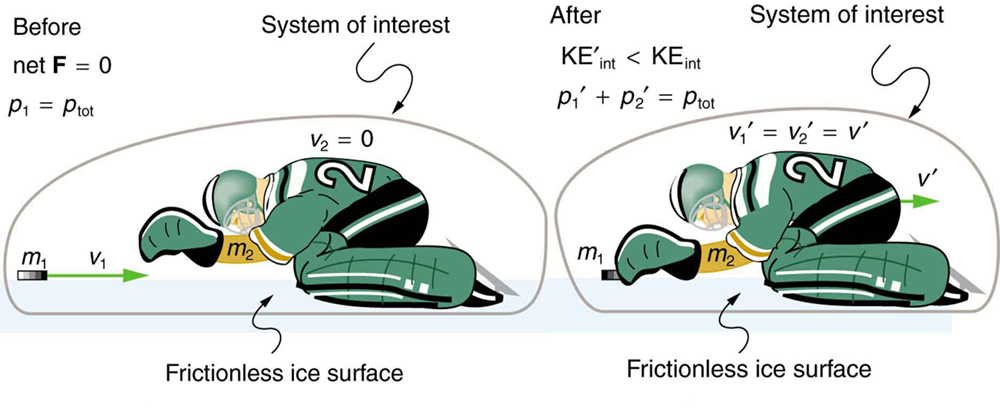
(a) Find the recoil velocity of a 70.0-kg ice hockey goalie, originally at rest, who catches a 0.150-kg hockey puck slapped at him at a velocity of 35.0 m/s. (b) How much kinetic energy is lost during the collision? Assume friction between the ice and the puck-goalie system is negligible. (See [link] )
Strategy
Momentum is conserved because the net external force on the puck-goalie system is zero. We can thus use conservation of momentum to find the final velocity of the puck and goalie system. Note that the initial velocity of the goalie is zero and that the final velocity of the puck and goalie are the same. Once the final velocity is found, the kinetic energies can be calculated before and after the collision and compared as requested.
Solution for (a)
Momentum is conserved because the net external force on the puck-goalie system is zero.
Conservation of momentum is
or
Because the goalie is initially at rest, we know . Because the goalie catches the puck, the final velocities are equal, or . Thus, the conservation of momentum equation simplifies to
Solving for yields
Entering known values in this equation, we get
Discussion for (a)
This recoil velocity is small and in the same direction as the puck’s original velocity, as we might expect.
Solution for (b)
Before the collision, the internal kinetic energy of the system is that of the hockey puck, because the goalie is initially at rest. Therefore, is initially

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?