| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
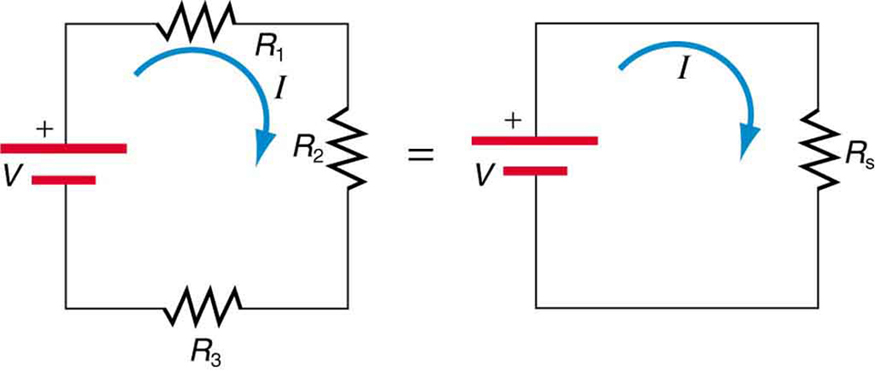
To verify that resistances in series do indeed add, let us consider the loss of electrical power, called a voltage drop , in each resistor in [link] .
According to Ohm’s law , the voltage drop, , across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation , where equals the current in amps (A) and is the resistance in ohms . Another way to think of this is that is the voltage necessary to make a current flow through a resistance .
So the voltage drop across is , that across is , and that across is . The sum of these voltages equals the voltage output of the source; that is,
This equation is based on the conservation of energy and conservation of charge. Electrical potential energy can be described by the equation , where is the electric charge and is the voltage. Thus the energy supplied by the source is , while that dissipated by the resistors is
The derivations of the expressions for series and parallel resistance are based on the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of charge, which state that total charge and total energy are constant in any process. These two laws are directly involved in all electrical phenomena and will be invoked repeatedly to explain both specific effects and the general behavior of electricity.
These energies must be equal, because there is no other source and no other destination for energy in the circuit. Thus, . The charge cancels, yielding , as stated. (Note that the same amount of charge passes through the battery and each resistor in a given amount of time, since there is no capacitance to store charge, there is no place for charge to leak, and charge is conserved.)
Now substituting the values for the individual voltages gives
Note that for the equivalent single series resistance , we have
This implies that the total or equivalent series resistance of three resistors is .
This logic is valid in general for any number of resistors in series; thus, the total resistance of a series connection is
as proposed. Since all of the current must pass through each resistor, it experiences the resistance of each, and resistances in series simply add up.
Suppose the voltage output of the battery in [link] is , and the resistances are , , and . (a) What is the total resistance? (b) Find the current. (c) Calculate the voltage drop in each resistor, and show these add to equal the voltage output of the source. (d) Calculate the power dissipated by each resistor. (e) Find the power output of the source, and show that it equals the total power dissipated by the resistors.
Strategy and Solution for (a)
The total resistance is simply the sum of the individual resistances, as given by this equation:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?