| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Fourier series representation of a periodic signal makes it easy to determine how a linear, time-invariant filter reshapessuch signals in general . The fundamental property of a linear system is that its input-output relationobeys superposition: . Because the Fourier series represents a periodic signal as alinear combination of complex exponentials, we can exploit the superposition property. Furthermore, we found for linearcircuits that their output to a complex exponential input is just the frequency response evaluated at the signal's frequencytimes the complex exponential. Said mathematically, if , then the output because . Thus, if is periodic thereby having a Fourier series, a linear circuit's output to this signal will be the superposition of the output toeach component.
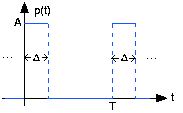
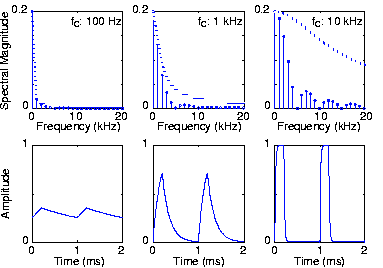
The periodic pulse signal shown on the left above serves as the input to a -circuit that has the transfer function (calculated elsewhere )
What is the average value of each output waveform? The correct answer may surprise you.
Because the filter's gain at zero frequency equals one, the average output values equal the respective average inputvalues.
This example also illustrates the impact a lowpass filter canhave on a waveform. The simple filter used here has a rather gradual frequency response, which means that higher harmonics are smoothly suppressed. Later, wewill describe filters that have much more rapidly varying frequency responses, allowing a much more dramatic selection ofthe input's Fourier coefficients.
More importantly, we have calculated the output of a circuit toa periodic input without writing, much less solving, the differential equation governing the circuit'sbehavior. Furthermore, we made these calculations entirely in the frequency domain. Using Fourier series, we can calculatehow any linear circuit will respond to a periodic input.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?