| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
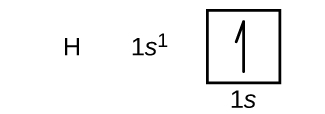
Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, m l = 0, ). The second electron also goes into the 1 s orbital and fills that orbital. The second electron has the same n , l , and m l quantum numbers, but must have the opposite spin quantum number, This is in accord with the Pauli exclusion principle: No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are:
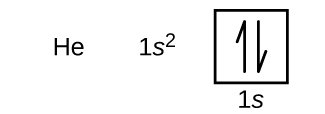
The n = 1 shell is completely filled in a helium atom.
The next atom is the alkali metal lithium with an atomic number of 3. The first two electrons in lithium fill the 1 s orbital and have the same sets of four quantum numbers as the two electrons in helium. The remaining electron must occupy the orbital of next lowest energy, the 2 s orbital ( [link] or [link] ). Thus, the electron configuration and orbital diagram of lithium are:
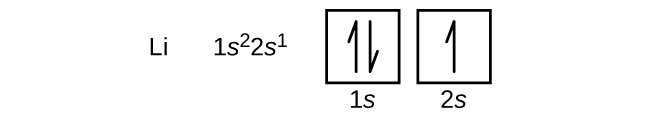
An atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus. The fourth electron fills the remaining space in the 2 s orbital.
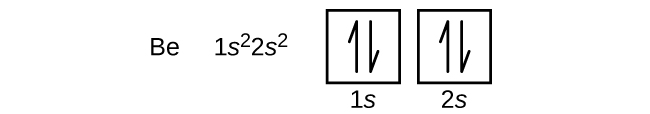
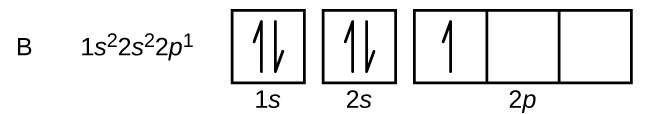
An atom of boron (atomic number 5) contains five electrons. The n = 1 shell is filled with two electrons and three electrons will occupy the n = 2 shell. Because any s subshell can contain only two electrons, the fifth electron must occupy the next energy level, which will be a 2 p orbital. There are three degenerate 2 p orbitals ( m l = −1, 0, +1) and the electron can occupy any one of these p orbitals. When drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same subshell that we are filling.
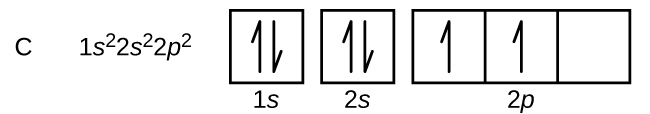
Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Four of them fill the 1 s and 2 s orbitals. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2 p subshell. We now have a choice of filling one of the 2 p orbitals and pairing the electrons or of leaving the electrons unpaired in two different, but degenerate, p orbitals. The orbitals are filled as described by Hund’s rule : the lowest-energy configuration for an atom with electrons within a set of degenerate orbitals is that having the maximum number of unpaired electrons. Thus, the two electrons in the carbon 2 p orbitals have identical n , l , and m s quantum numbers and differ in their m l quantum number (in accord with the Pauli exclusion principle). The electron configuration and orbital diagram for carbon are:
Nitrogen (atomic number 7) fills the 1 s and 2 s subshells and has one electron in each of the three 2 p orbitals, in accordance with Hund’s rule. These three electrons have unpaired spins. Oxygen (atomic number 8) has a pair of electrons in any one of the 2 p orbitals (the electrons have opposite spins) and a single electron in each of the other two. Fluorine (atomic number 9) has only one 2 p orbital containing an unpaired electron. All of the electrons in the noble gas neon (atomic number 10) are paired, and all of the orbitals in the n = 1 and the n = 2 shells are filled. The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?