| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
A monetary policy that lowers interest rates and stimulates borrowing is known as an expansionary monetary policy or loose monetary policy . Conversely, a monetary policy that raises interest rates and reduces borrowing in the economy is a contractionary monetary policy or tight monetary policy . This module will discuss how expansionary and contractionary monetary policies affect interest rates and aggregate demand, and how such policies will affect macroeconomic goals like unemployment and inflation. We will conclude with a look at the Fed’s monetary policy practice in recent decades.
Consider the market for loanable bank funds, shown in [link] . The original equilibrium (E 0 ) occurs at an interest rate of 8% and a quantity of funds loaned and borrowed of $10 billion. An expansionary monetary policy will shift the supply of loanable funds to the right from the original supply curve (S 0 ) to S 1 , leading to an equilibrium (E 1 ) with a lower interest rate of 6% and a quantity of funds loaned of $14 billion. Conversely, a contractionary monetary policy will shift the supply of loanable funds to the left from the original supply curve (S 0 ) to S 2 , leading to an equilibrium (E 2 ) with a higher interest rate of 10% and a quantity of funds loaned of $8 billion.
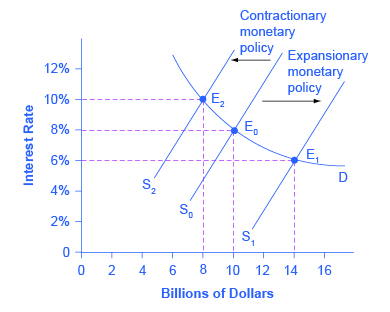
So how does a central bank “raise” interest rates? When describing the monetary policy actions taken by a central bank, it is common to hear that the central bank “raised interest rates” or “lowered interest rates.” We need to be clear about this: more precisely, through open market operations the central bank changes bank reserves in a way which affects the supply curve of loanable funds. As a result, interest rates change, as shown in [link] . If they do not meet the Fed’s target, the Fed can supply more or less reserves until interest rates do.
Recall that the specific interest rate the Fed targets is the federal funds rate . The Federal Reserve has, since 1995, established its target federal funds rate in advance of any open market operations.
Of course, financial markets display a wide range of interest rates , representing borrowers with different risk premiums and loans that are to be repaid over different periods of time. In general, when the federal funds rate drops substantially, other interest rates drop, too, and when the federal funds rate rises, other interest rates rise. However, a fall or rise of one percentage point in the federal funds rate—which remember is for borrowing overnight—will typically have an effect of less than one percentage point on a 30-year loan to purchase a house or a three-year loan to purchase a car. Monetary policy can push the entire spectrum of interest rates higher or lower, but the specific interest rates are set by the forces of supply and demand in those specific markets for lending and borrowing.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University of houston downtown: macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?