| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Keynesian perspective focuses on aggregate demand. The idea is simple: firms produce output only if they expect it to sell. Thus, while the availability of the factors of production determines a nation’s potential GDP , the amount of goods and services actually being sold, known as real GDP , depends on how much demand exists across the economy. This point is illustrated in [link] .
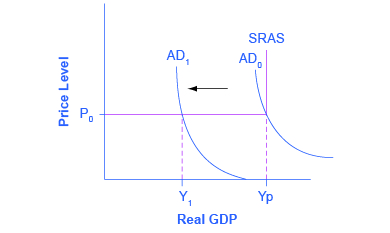
Keynes argued that, for reasons we explain shortly, aggregate demand is not stable—that it can change unexpectedly. Suppose the economy starts where AD intersects SRAS at P 0 and Yp. Because Yp is potential output, the economy is at full employment. Because AD is volatile, it can easily fall. Thus, even if we start at Yp, if AD falls, then we find ourselves in what Keynes termed a recessionary gap . The economy is in equilibrium but with less than full employment, as shown at Y 1 in the [link] . Keynes believed that the economy would tend to stay in a recessionary gap, with its attendant unemployment, for a significant period of time.
In the same way (though not shown in the figure), if AD increases, the economy could experience an inflationary gap , where demand is attempting to push the economy past potential output. As a consequence, the economy experiences inflation. The key policy implication for either situation is that government needs to step in and close the gap, increasing spending during recessions and decreasing spending during booms to return aggregate demand to match potential output.
Recall from The Aggregate Supply-Aggregate Demand Model that aggregate demand is total spending, economy-wide, on domestic goods and services. (Aggregate demand (AD) is actually what economists call total planned expenditure. Read the appendix on The Expenditure-Output Model for more on this.) You may also remember that aggregate demand is the sum of four components: consumption expenditure, investment expenditure, government spending, and spending on net exports (exports minus imports). In the following sections, we will examine each component through the Keynesian perspective.
Consumption expenditure is spending by households and individuals on durable goods, nondurable goods, and services. Durable goods are things that last and provide value over time, such as automobiles. Nondurable goods are things like groceries—once you consume them, they are gone. Recall from The Macroeconomic Perspective that services are intangible things consumers buy, like healthcare or entertainment.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of macroeconomics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?