| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[link] involved finding the area inside one curve. We can also use [link] to find the area between two polar curves. However, we often need to find the points of intersection of the curves and determine which function defines the outer curve or the inner curve between these two points.
Find the area outside the cardioid and inside the circle
First draw a graph containing both curves as shown.
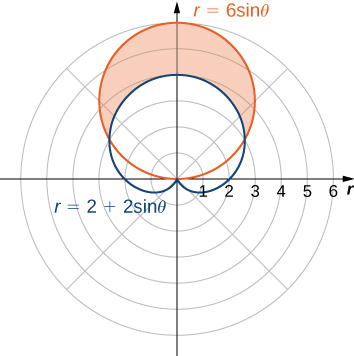
To determine the limits of integration, first find the points of intersection by setting the two functions equal to each other and solving for
This gives the solutions and which are the limits of integration. The circle is the red graph, which is the outer function, and the cardioid is the blue graph, which is the inner function. To calculate the area between the curves, start with the area inside the circle between and then subtract the area inside the cardioid between and
In [link] we found the area inside the circle and outside the cardioid by first finding their intersection points. Notice that solving the equation directly for yielded two solutions: and However, in the graph there are three intersection points. The third intersection point is the origin. The reason why this point did not show up as a solution is because the origin is on both graphs but for different values of For example, for the cardioid we get
so the values for that solve this equation are where n is any integer. For the circle we get
The solutions to this equation are of the form for any integer value of n. These two solution sets have no points in common. Regardless of this fact, the curves intersect at the origin. This case must always be taken into consideration.
Here we derive a formula for the arc length of a curve defined in polar coordinates.
In rectangular coordinates, the arc length of a parameterized curve for is given by
In polar coordinates we define the curve by the equation where In order to adapt the arc length formula for a polar curve, we use the equations
and we replace the parameter t by Then
We replace by and the lower and upper limits of integration are and respectively. Then the arc length formula becomes

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?