| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The case structure allows data to flow based on a integer, Boolean or string matching condition. The case executed is selected based on the data wired to the Case Selector .
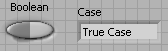
In the Front Panel window, select a Boolean control and an output string.

Arrange the diagram to look as in [link] .
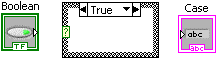
In the True case, add a string constant containing True Case .
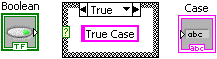
To select the False case, click on the selector label down arrow and select False from the pop-up menu. You can also cycle through the cases by clicking the next (right) or previous (left) arrows.

In the False case, add a string constant containing False Case .

Wire the string constant in the case structure to the output string terminal.

Select the True case and wire the string constant to the case structure tunnel . Complete the diagram as shown in [link] .

It is important to note that all instances in a case structure must be wired to enable data to flow from the case structure .
In the Front Panel window, toggle the Boolean input control and run the program.
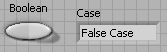
Select an Integer 32 numeric input and an Integer 32 numeric output and label them Selector and Case respectively.
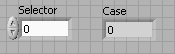
In the Block Diagram window, create a case structure , select the False case and arrange the terminals as shown in [link] .
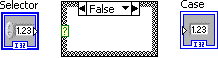
Wire the Selector numeric control to the case selector on the case structure. The selector label reflects the diagram update.

In the 0, Default case, add a numeric constant and leave its value as 0.
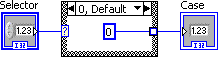
Using the selector label , select case 1. Add a numeric constant, enter 1 and wire it to the case tunnel. The resulting diagram is shown in [link] .
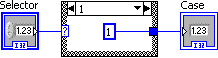
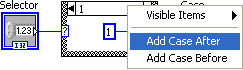
Right click anywhere in the case structure and select Add Case After from the pop-up menu.
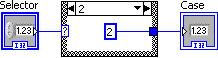
Case 2 is added after case 1. Add a numeric constant, enter 2 and wire it to the case structure tunnel.
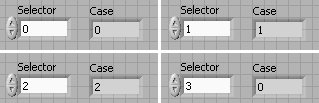
[link] shows the results of running this simple case selection programs for Selector set to 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
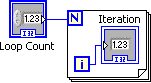
The For Loop structure repeatedly executes the diagram within the structure. The Loop Count specifies the number of times the loop contents must be executed and the Loop Iteration indicates which iteration is currently being executed.
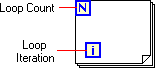
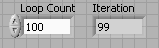
The Loop Count and Loop Iteration are of Integer 32 data types. If the Loop Count is set to N , then the Loop Iteration value range is from 0 to N-1 . This is illustrated in [link] and [link] .
Shift Registers allow the preservation of intermediate results between sequences of iterations.
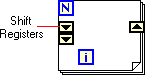
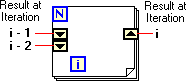
To add a Shift Register , right click on the For Loop structure and select Add Shift Register from the pop-up menu.
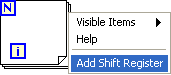
To add elements to the shift register , right click on the shift register and select Add Element from the pop-up menu.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to g programming' conversation and receive update notifications?