| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why can some humans harbor opportunistic pathogens like Haemophilus influenzae , Staphylococcus aureus , or Streptococcus pyogenes , in their upper respiratory tracts but remain asymptomatic carriers, while other individuals become seriously ill when infected? There is evidence suggesting that differences in susceptibility to infection between patients may be a result, at least in part, of genetic differences between human hosts. For example, genetic differences in human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) and red blood cell antigens among hosts have been implicated in different immune responses and resulting disease progression from infection with H. influenzae .
Because the genetic interplay between pathogen and host may contribute to disease outcomes, understanding differences in genetic makeup between individuals may be an important clinical tool. Ecological genomics is a relatively new field that seeks to understand how the genotypes of different organisms interact with each other in nature. The field answers questions about how gene expression of one organism affects gene expression of another. Medical applications of ecological genomics will focus on how pathogens interact with specific individuals, as opposed to humans in general. Such analyses would allow medical professionals to use knowledge of an individual’s genotype to apply more individualized plans for treatment and prevention of disease.
With the advent of next-generation sequencing, it is relatively easy to obtain the entire genomic sequences of pathogens; a bacterial genome can be sequenced in as little as a day. D.J. Edwards, K.E. Holt. “Beginner’s Guide to Comparative Bacterial Genome Analysis Using Next-Generation Sequence Data.” Microbial Informatics and Experimentation 3 no. 1 (2013):2. The speed and cost of sequencing the human genome has also been greatly reduced and, already, individuals can submit samples to receive extensive reports on their personal genetic traits, including ancestry and carrier status for various genetic diseases. As sequencing technologies progress further, such services will continue to become less expensive, more extensive, and quicker.
However, as this day quickly approaches, there are many ethical concerns with which society must grapple. For example, should genome sequencing be a standard practice for everybody? Should it be required by law or by employers if it will lower health-care costs? If one refuses genome sequencing, does he or she forfeit his or her right to health insurance coverage? For what purposes should the data be used? Who should oversee proper use of these data? If genome sequencing reveals predisposition to a particular disease, do insurance companies have the right to increase rates? Will employers treat an employee differently? Knowing that environmental influences also affect disease development, how should the data on the presence of a particular disease-causing allele in an individual be used ethically? The Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008 (GINA) currently prohibits discriminatory practices based on genetic information by both health insurance companies and employers. However, GINA does not cover life, disability, or long-term care insurance policies. Clearly, all members of society must continue to engage in conversations about these issues so that such genomic data can be used to improve health care while simultaneously protecting an individual’s rights.
Cells are always producing proteins from every gene they possess.
False
The process of making an RNA copy of a gene is called ________.
transcription
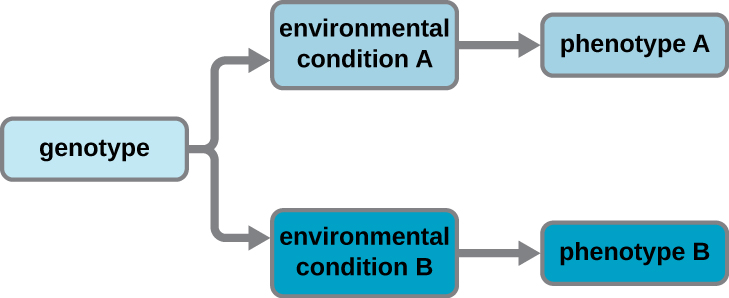
A cell’s ________ remains constant whereas its phenotype changes in response to environmental influences.
genotype or genome
Can two observably different cells have the same genotype? Explain.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?