| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All cellular life has a DNA genome organized into one or more chromosomes. Prokaryotic chromosomes are typically circular, haploid (unpaired), and not bound by a complex nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic DNA and DNA-associated proteins are concentrated within the nucleoid region of the cell ( [link] ). In general, prokaryotic DNA interacts with nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs) that assist in the organization and packaging of the chromosome. In bacteria, NAPs function similar to histones, which are the DNA-organizing proteins found in eukaryotic cells. In archaea, the nucleoid is organized by either NAPs or histone-like DNA organizing proteins.
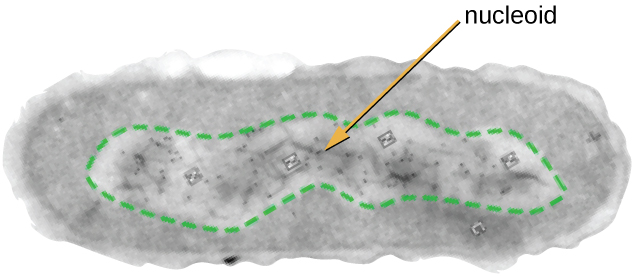
Prokaryotic cells may also contain extrachromosomal DNA, or DNA that is not part of the chromosome. This extrachromosomal DNA is found in plasmid s , which are small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules. Cells that have plasmids often have hundreds of them within a single cell. Plasmids are more commonly found in bacteria; however, plasmids have been found in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. Plasmids often carry genes that confer advantageous traits such as antibiotic resistance; thus, they are important to the survival of the organism. We will discuss plasmids in more detail in Mechanisms of Microbial Genetics .
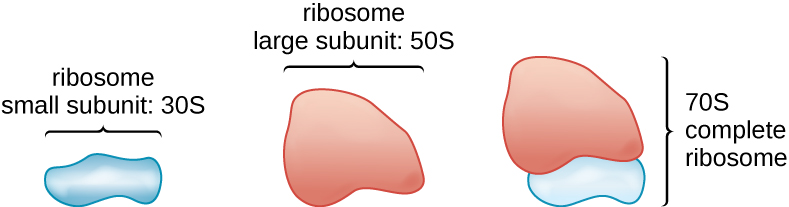
All cellular life synthesizes proteins, and organisms in all three domains of life possess ribosomes, structures responsible protein synthesis. However, ribosomes in each of the three domains are structurally different. Ribosomes, themselves, are constructed from proteins, along with ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Prokaryotic ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm. They are called 70S ribosome s because they have a size of 70S ( [link] ), whereas eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes have a size of 80S. (The S stands for Svedberg unit, a measure of sedimentation in an ultracentrifuge, which is based on size, shape, and surface qualities of the structure being analyzed). Although they are the same size, bacterial and archaeal ribosomes have different proteins and rRNA molecules, and the archaeal versions are more similar to their eukaryotic counterparts than to those found in bacteria.
As single-celled organisms living in unstable environments, some prokaryotic cells have the ability to store excess nutrients within cytoplasmic structures called inclusions . Storing nutrients in a polymerized form is advantageous because it reduces the buildup of osmotic pressure that occurs as a cell accumulates solutes. Various types of inclusions store glycogen and starches, which contain carbon that cells can access for energy. Volutin granules, also called metachromatic granules because of their staining characteristics, are inclusions that store polymerized inorganic phosphate that can be used in metabolism and assist in the formation of biofilms. Microbes known to contain volutin granules include the archaea Methanosarcina , the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae , and the unicellular eukaryotic alga Chlamydomonas . Sulfur granules, another type of inclusion, are found in sulfur bacteria of the genus Thiobacillus ; these granules store elemental sulfur, which the bacteria use for metabolism.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?