| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Alcohols tend to be bactericidal and fungicidal, but may also be viricidal for enveloped viruses only. Although alcohols are not sporicidal, they do inhibit the processes of sporulation and germination. Alcohols are volatile and dry quickly, but they may also cause skin irritation because they dehydrate the skin at the site of application. One common clinical use of alcohols is swabbing the skin for degerming before needle injection. Alcohols also are the active ingredients in instant hand sanitizer s, which have gained popularity in recent years. The alcohol in these hand sanitizers works both by denaturing proteins and by disrupting the microbial cell membrane, but will not work effectively in the presence of visible dirt.
Last, alcohols are used to make tincture s with other antiseptics, such as the iodine tinctures discussed previously in this chapter. All in all, alcohols are inexpensive and quite effective for the disinfection of a broad range of vegetative microbes. However, one disadvantage of alcohols is their high volatility, limiting their effectiveness to immediately after application.

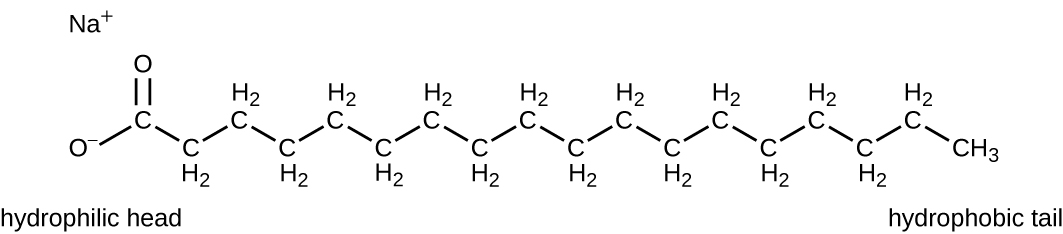
Surface-active agents, or surfactants , are a group of chemical compounds that lower the surface tension of water. Surfactants are the major ingredients in soaps and detergents . Soaps are salts of long-chain fatty acids and have both polar and nonpolar regions, allowing them to interact with polar and nonpolar regions in other molecules ( [link] ). They can interact with nonpolar oils and grease to create emulsions in water, loosening and lifting away dirt and microbes from surfaces and skin. Soaps do not kill or inhibit microbial growth and so are not considered antiseptics or disinfectants. However, proper use of soaps mechanically carries away microorganisms, effectively degerming a surface. Some soaps contain added bacteriostatic agents such as triclocarban or cloflucarban , compounds structurally related to triclosan, that introduce antiseptic or disinfectant properties to the soaps.
Soaps, however, often form films that are difficult to rinse away, especially in hard water, which contains high concentrations of calcium and magnesium mineral salts. Detergents contain synthetic surfactant molecules with both polar and nonpolar regions that have strong cleansing activity but are more soluble, even in hard water, and, therefore, leave behind no soapy deposits. Anionic detergents , such as those used for laundry, have a negatively charged anion at one end attached to a long hydrophobic chain, whereas cationic detergents have a positively charged cation instead. Cationic detergents include an important class of disinfectants and antiseptics called the quaternary ammonium salts (quats) , named for the characteristic quaternary nitrogen atom that confers the positive charge ( [link] ). Overall, quats have properties similar to phospholipids, having hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends. As such, quats have the ability to insert into the bacterial phospholipid bilayer and disrupt membrane integrity. The cationic charge of quats appears to confer their antimicrobial properties, which are diminished when neutralized. Quats have several useful properties. They are stable, nontoxic, inexpensive, colorless, odorless, and tasteless. They tend to be bactericidal by disrupting membranes. They are also active against fungi, protozoans, and enveloped viruses, but endospores are unaffected. In clinical settings, they may be used as antiseptics or to disinfect surfaces. Mixtures of quats are also commonly found in household cleaners and disinfectants, including many current formulations of Lysol brand products, which contain benzalkonium chlorides as the active ingredients. Benzalkonium chlorides, along with the quat cetylpyrimidine chloride , are also found in products such as skin antiseptics, oral rinses, and mouthwashes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?