| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
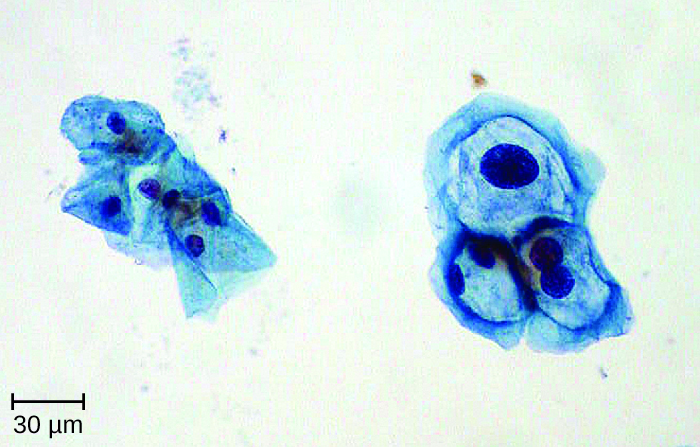
Most HPV infections resolve spontaneously; however, various therapies are used to treat and remove warts. Topical medications such as imiquimod (which stimulates the production of interferon), podofilox , or sinecatechins , may be effective. Warts can also be removed using cryotherapy or surgery, but these approaches are less effective for genital warts than for other types of warts. Electrocauterization and carbon dioxide laser therapy are also used for wart removal.
Regular Pap testing can detect abnormal cells that might progress to cervical cancer, followed by biopsy and appropriate treatment. Vaccines for some of the high risk HPV types are now available. Gardasil vaccine includes types 6, 11, 16 and 18 (types 6 and 11 are associated with 90% of genital wart infections and types 16 and 18 are associated with 70% of cervical cancers). Gardasil 9 vaccinates against the previous four types and an additional five high-risk types (31, 33, 45, 52, and 58). Cervarix vaccine includes just HPV types 16 and 18. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent infection with oncogenic HPV, but it is important to note that not all oncogenic HPV types are covered by the available vaccines. It is recommended for both boys and girls prior to sexual activity (usually between the ages of nine and fifteen).

Watch a video of how perceptions of HPV affect vaccination rates.
Few people who have an STI (or think they may have one) are eager to share that information publicly. In fact, many patients are even uncomfortable discussing the symptoms privately with their doctors. Unfortunately, the social stigma associated with STIs makes it harder for infected individuals to seek the treatment they need and creates the false perception that STIs are rare. In reality, STIs are quite common, but it is difficult to determine exactly how common.
A recent study on the effects of HPV vaccination found a baseline HPV prevalence of 26.8% for women between the ages of 14 and 59. Among women aged 20–24, the prevalence was 44.8%; in other words, almost half of the women in this age bracket had a current infection. Eileen F. Dunne, Elizabeth R. Unger, Maya Sternberg, Geraldine McQuillan, David C. Swan, Sonya S. Patel, and Lauri E. Markowitz. “Prevalence of HPV Infection Among Females in the United States.” Journal of the American Medical Association 297, no. 8 (2007): 813–819. According to the CDC, HSV-2 infection was estimated to have a prevalence of 15.5% in younger individuals (14–49 years of age) in 2007–2010, down from 20.3% in the same age group in 1988–1994. However, the CDC estimates that 87.4% of infected individuals in this age group have not been diagnosed by a physician. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Genital Herpes - CDC Fact Sheet,” 2015. http://www.cdc.gov/std/herpes/stdfact-herpes-detailed.htm.
Another complicating factor is that many STIs can be asymptomatic or have long periods of latency. For example, the CDC estimates that among women ages 14–49 in the United States, about 2.3 million (3.1%) are infected with the sexually transmitted protozoan Trichomonas (see Protozoan Infections of the Urogenital System ); however, in a study of infected women, 85% of those diagnosed with the infection were asymptomatic. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Trichomoniasis Statistics,” 2015. http://www.cdc.gov/std/trichomonas/stats.htm.
Even when patients are treated for symptomatic STIs, it can be difficult to obtain accurate data on the number of cases. Whereas STIs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are notifiable diseases—meaning each diagnosis must be reported by healthcare providers to the CDC—other STIs are not notifiable (e.g., genital herpes, genital warts, and trichomoniasis). Between the social taboos, the inconsistency of symptoms, and the lack of mandatory reporting, it can be difficult to estimate the true prevalence of STIs—but it is safe to say they are much more prevalent than most people think.
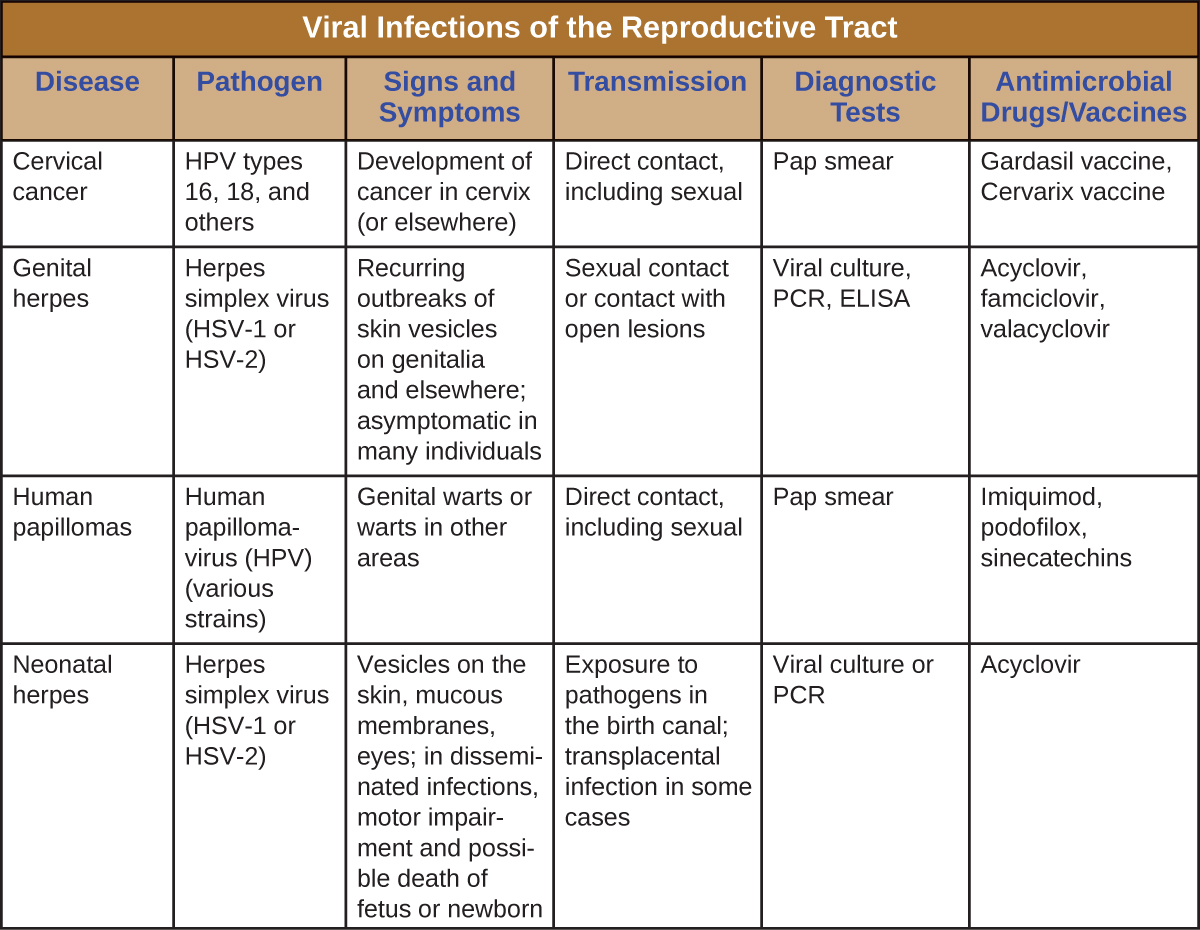
[link] summarizes the most important features of viral diseases affecting the human reproductive tract.
Is it true that human papillomaviruses can always be detected by the presence of genital warts?
How is neonatal herpes transmitted?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?