| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
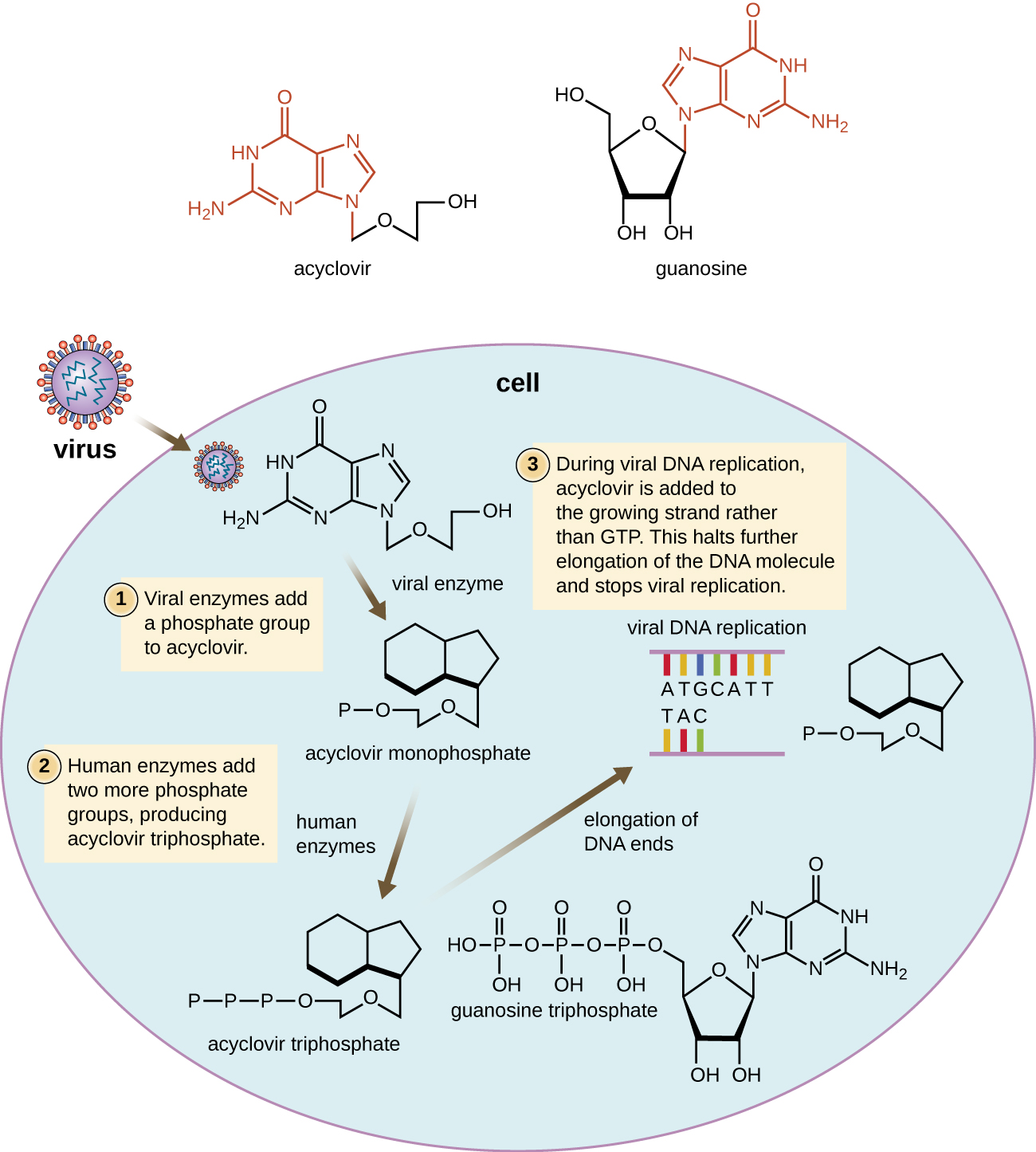
| Common Antiviral Drugs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Drug | Clinical Uses |
| Nucleoside analog inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis | Acyclovir | Herpes virus infections |
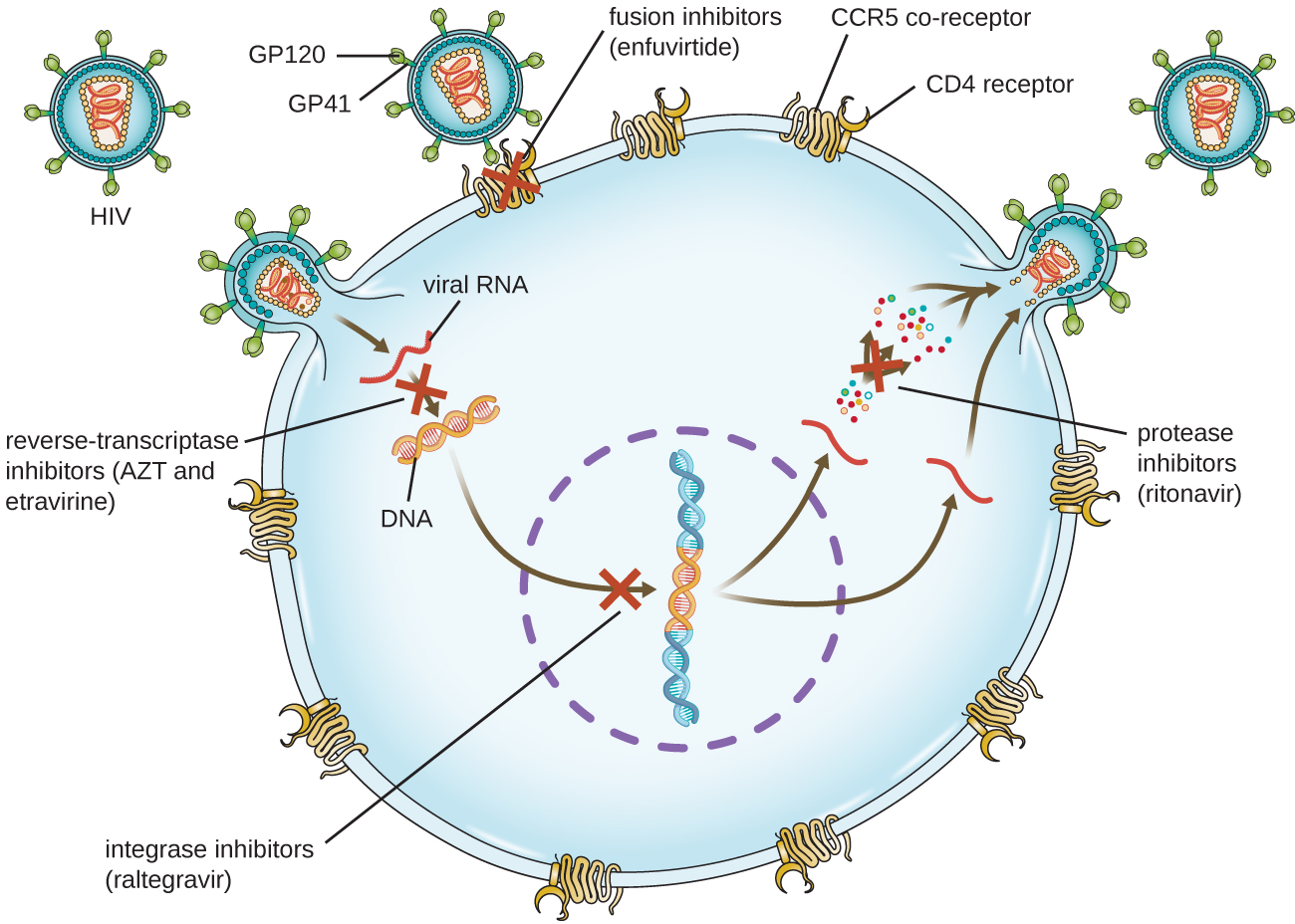
| Azidothymidine/zidovudine (AZT) | HIV infections | |
| Ribavirin | Hepatitis C virus and respiratory syncytial virus infections | |
| Vidarabine | Herpes virus infections | |
| Sofosbuvir | Hepatitis C virus infections | |
| Non-nucleoside noncompetitive inhibition | Etravirine | HIV infections |
| Inhibit escape of virus from endosomes | Amantadine, rimantadine | Infections with influenza virus |
| Inhibit neuraminadase | Olsetamivir, zanamivir, peramivir | Infections with influenza virus |
| Inhibit viral uncoating | Pleconaril | Serious enterovirus infections |
| Inhibition of protease | Ritonavir | HIV infections |
| Simeprevir | Hepatitis C virus infections | |
| Inhibition of integrase | Raltegravir | HIV infections |
| Inhibition of membrane fusion | Enfuviritide | HIV infections |

To learn more about the various classes of antiretroviral drugs used in the ART of HIV infection, explore each of the drugs in the HIV drug classes provided by US Department of Health and Human Services at this website.
Antiviral drugs, like Tamiflu and Relenza, that are effective against the influenza virus by preventing viral escape from host cells are called ________.
neuraminidase inhibitors
Echinocandins, known as “penicillin for fungi,” target β(1→3) glucan in fungal cell walls.
true
How does the biology of HIV necessitate the need to treat HIV infections with multiple drugs?
Niclosamide is insoluble and thus is not readily absorbed from the stomach into the bloodstream. How does the insolubility of niclosamide aid its effectiveness as a treatment for tapeworm infection?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?