| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
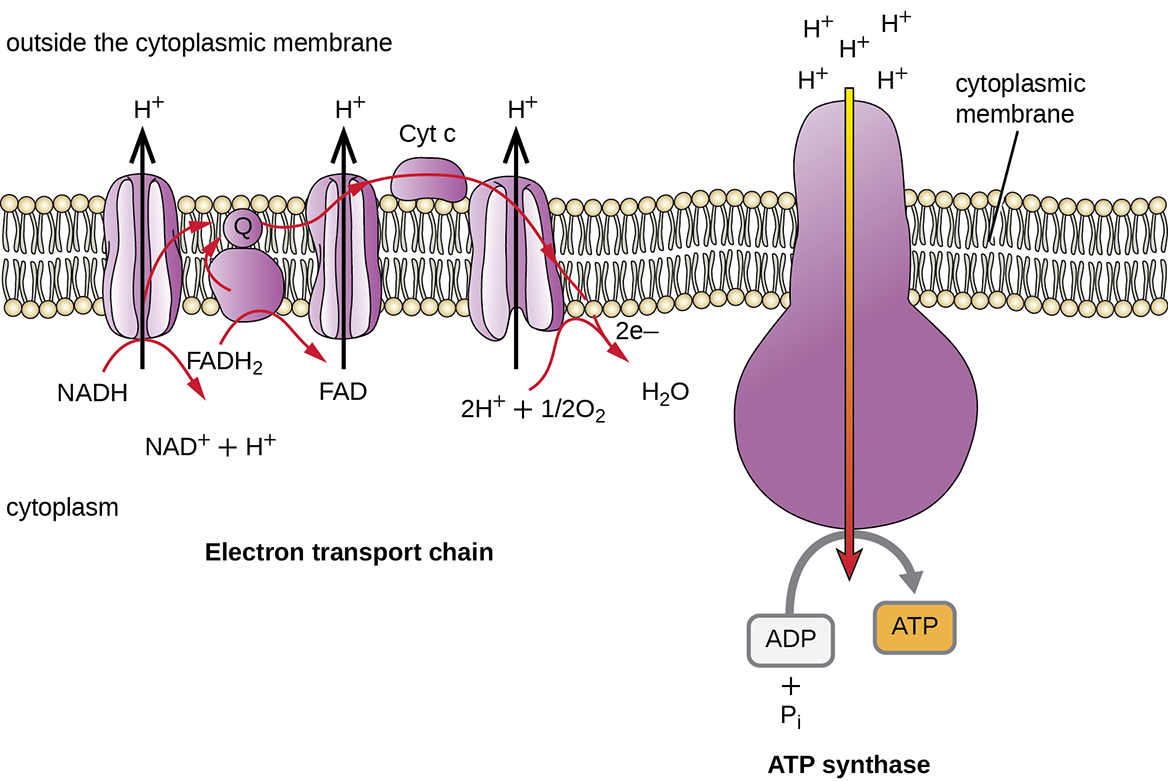
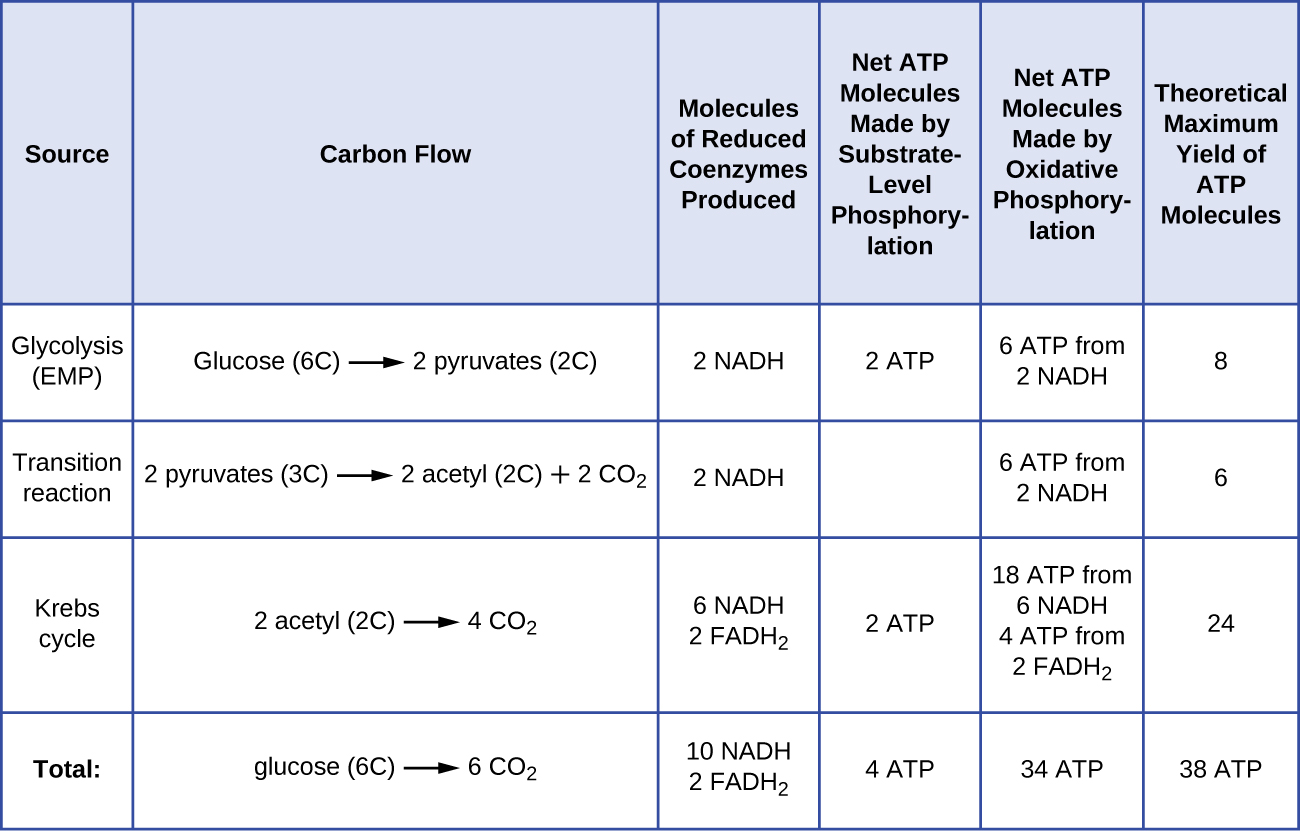
The number of ATP molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. For example, the number of hydrogen ions that the electron transport system complexes can pump through the membrane varies between different species of organisms. In aerobic respiration in mitochondria, the passage of electrons from one molecule of NADH generates enough proton motive force to make three ATP molecules by oxidative phosphorylation, whereas the passage of electrons from one molecule of FADH 2 generates enough proton motive force to make only two ATP molecules. Thus, the 10 NADH molecules made per glucose during glycolysis, the transition reaction, and the Krebs cycle carry enough energy to make 30 ATP molecules, whereas the two FADH 2 molecules made per glucose during these processes provide enough energy to make four ATP molecules. Overall, the theoretical maximum yield of ATP made during the complete aerobic respiration of glucose is 38 molecules, with four being made by substrate-level phosphorylation and 34 being made by oxidative phosphorylation ( [link] ). In reality, the total ATP yield is usually less, ranging from one to 34 ATP molecules, depending on whether the cell is using aerobic respiration or anaerobic respiration; in eukaryotic cells, some energy is expended to transport intermediates from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria, affecting ATP yield.
[link] summarizes the theoretical maximum yields of ATP from various processes during the complete aerobic respiration of one glucose molecule.
The final ETS complex used in aerobic respiration that transfers energy-depleted electrons to oxygen to form H 2 O is called ________.
cytochrome oxidase
The passage of hydrogen ions through ________ down their electrochemical gradient harnesses the energy needed for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation.
ATP synthase
All organisms that use aerobic cellular respiration have cytochrome oxidase.
True
What is the relationship between chemiosmosis and the proton motive force?
How does oxidative phosphorylation differ from substrate-level phosphorylation?
How does the location of ATP synthase differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Where do protons accumulate as a result of the ETS in each cell type?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?