| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Most of the mistakes introduced during DNA replication are promptly corrected by most DNA polymerase s through a function called proofreading. In proofreading , the DNA polymerase reads the newly added base, ensuring that it is complementary to the corresponding base in the template strand before adding the next one. If an incorrect base has been added, the enzyme makes a cut to release the wrong nucleotide and a new base is added.
Some errors introduced during replication are corrected shortly after the replication machinery has moved. This mechanism is called mismatch repair . The enzymes involved in this mechanism recognize the incorrectly added nucleotide, excise it, and replace it with the correct base. One example is the methyl-directed mismatch repair in E. coli . The DNA is hemimethylated. This means that the parental strand is methylated while the newly synthesized daughter strand is not. It takes several minutes before the new strand is methylated. Proteins MutS, MutL, and MutH bind to the hemimethylated site where the incorrect nucleotide is found. MutH cuts the nonmethylated strand (the new strand). An exonuclease removes a portion of the strand (including the incorrect nucleotide). The gap formed is then filled in by DNA pol III and ligase.
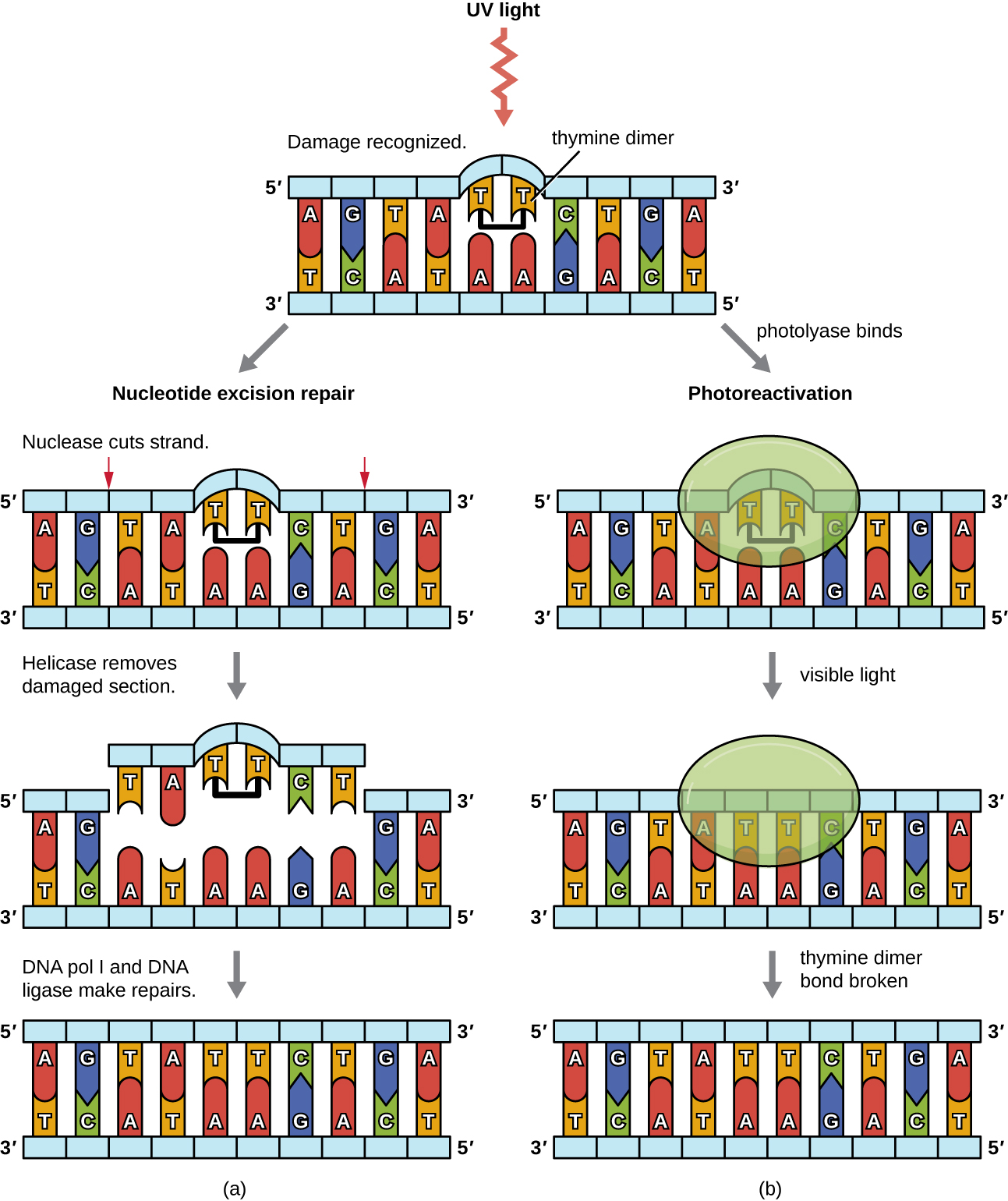
Because the production of thymine dimer s is common (many organisms cannot avoid ultraviolet light), mechanisms have evolved to repair these lesions. In nucleotide excision repair (also called dark repair), enzymes remove the pyrimidine dimer and replace it with the correct nucleotides ( [link] ). In E. coli , the DNA is scanned by an enzyme complex. If a distortion in the double helix is found that was introduced by the pyrimidine dimer, the enzyme complex cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone several bases upstream and downstream of the dimer, and the segment of DNA between these two cuts is then enzymatically removed. DNA pol I replaces the missing nucleotides with the correct ones and DNA ligase seals the gap in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
The direct repair (also called light repair) of thymine dimers occurs through the process of photoreactivation in the presence of visible light. An enzyme called photolyase recognizes the distortion in the DNA helix caused by the thymine dimer and binds to the dimer. Then, in the presence of visible light, the photolyase enzyme changes conformation and breaks apart the thymine dimer, allowing the thymines to again correctly base pair with the adenines on the complementary strand. Photoreactivation appears to be present in all organisms, with the exception of placental mammals, including humans. Photoreactivation is particularly important for organisms chronically exposed to ultraviolet radiation , like plants, photosynthetic bacteria, algae, and corals, to prevent the accumulation of mutations caused by thymine dimer formation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?