| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
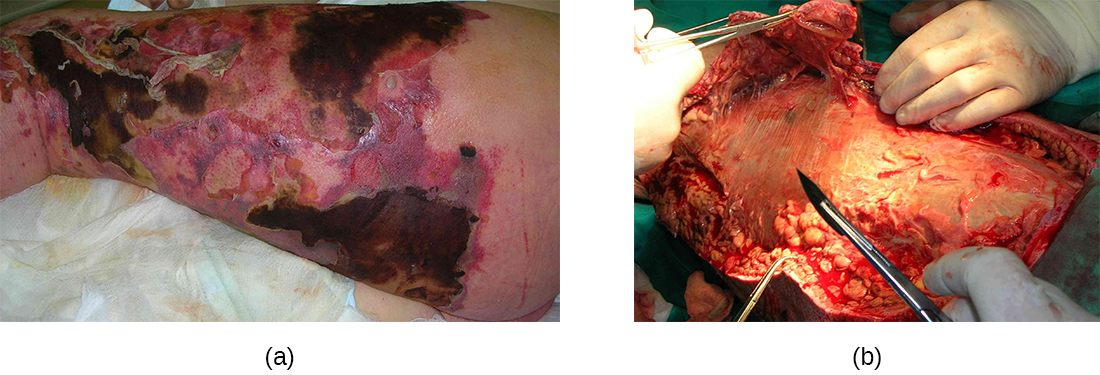
Streptococcal infections that start in the skin can sometimes spread elsewhere, resulting in a rare but potentially life-threatening condition called necrotizing fasciitis , sometimes referred to as flesh-eating bacterial syndrome . S. pyogenes is one of several species that can cause this rare but potentially-fatal condition; others include Klebsiella , Clostridium , Escherichia coli , S. aureus , and Aeromonas hydrophila .
Necrotizing fasciitis occurs when the fascia, a thin layer of connective tissue between the skin and muscle, becomes infected. Severe invasive necrotizing fasciitis due to Streptococcus pyogenes occurs when virulence factors that are responsible for adhesion and invasion overcome host defenses. S. pyogenes invasins allow bacterial cells to adhere to tissues and establish infection. Bacterial proteases unique to S. pyogenes aggressively infiltrate and destroy host tissues, inactivate complement, and prevent neutrophil migration to the site of infection. The infection and resulting tissue death can spread very rapidly, as large areas of skin become detached and die. Treatment generally requires debridement (surgical removal of dead or infected tissue) or amputation of infected limbs to stop the spread of the infection; surgical treatment is supplemented with intravenous antibiotics and other therapies ( [link] ).
Necrotizing fasciitis does not always originate from a skin infection; in some cases there is no known portal of entry. Some studies have suggested that experiencing a blunt force trauma can increase the risk of developing streptococcal necrotizing fasciitis. Nuwayhid, Z.B., Aronoff, D.M., and Mulla, Z.D.. “Blunt Trauma as a Risk Factor for Group A Streptococcal Necrotizing Fasciitis.” Annals of Epidemiology (2007) 17:878–881.
Observing that Sam’s wound is purulent, the doctor tells him that he probably has a bacterial infection. She takes a sample from the lesion to send for laboratory analysis, but because it is Friday, she does not expect to receive the results until the following Monday. In the meantime, she prescribes an over-the-counter topical antibiotic ointment. She tells Sam to keep the wound clean and apply a new bandage with the ointment at least twice per day.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
Another important skin pathogen is Pseudomonas aeruginosa , a gram-negative, oxidase-positive, aerobic bacillus that is commonly found in water and soil as well as on human skin. P. aeruginosa is a common cause of opportunistic infections of wounds and burns. It can also cause hot tub rash , a condition characterized by folliculitis that frequently afflicts users of pools and hot tubs (recall the Clinical Focus case in Microbial Biochemistry ). P. aeruginosa is also the cause of otitis externa ( swimmer’s ear ), an infection of the ear canal that causes itching, redness, and discomfort, and can progress to fever, pain, and swelling ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?