| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
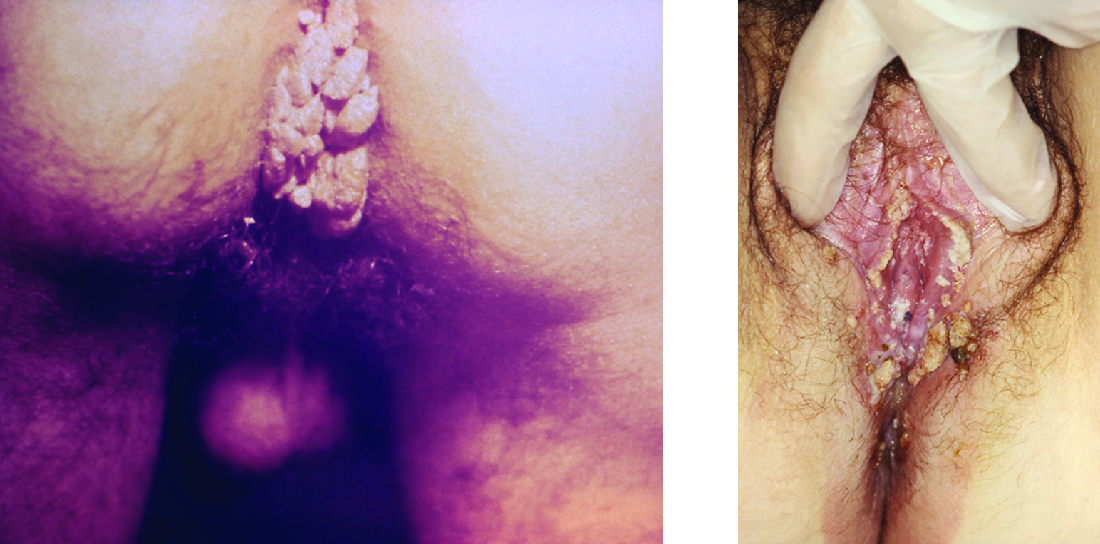
Warts of all types are caused by a variety of strains of human papillomavirus (HPV) (see Viral Infections of the Skin and Eyes ). Condylomata acuminata, more commonly called genital warts or venereal warts ( [link] ), are an extremely prevalent STI caused by certain strains of HPV. Condylomata are irregular, soft, pink growths that are found on external genitalia or the anus.
HPV is a small, non-enveloped virus with a circular double-stranded DNA genome. Researchers have identified over 200 different strains (called types) of HPV, with approximately 40 causing STIs. While some types of HPV cause genital warts, HPV infection is often asymptomatic and self-limiting. However, genital HPV infection often co-occurs with other STIs like syphilis or gonorrhea. Additionally, some forms of HPV (not the same ones associated with genital warts) are associated with cervical cancers . At least 14 oncogenic (cancer-causing) HPV types are known to have a causal association with cervical cancers. Examples of oncogenic HPV are types 16 and 18, which are associated with 70% of cervical cancers. Lauren Thaxton and Alan G. Waxman. “Cervical Cancer Prevention: Immunization and Screening 2015.” Medical Clinics of North America 99, no. 3 (2015): 469–477. Oncogenic HPV types can also cause oropharyngeal cancer, anal cancer, vaginal cancer, vulvar cancer, and penile cancer. Most of these cancers are caused by HPV type 16. HPV virulence factors include proteins (E6 and E7) that are capable of inactivating tumor suppressor proteins, leading to uncontrolled cell division and the development of cancer.
HPV cannot be cultured, so molecular tests are the primary method used to detect HPV. While routine HPV screening is not recommended for men, it is included in guidelines for women. An initial screening for HPV at age 30, conducted at the same time as a Pap test , is recommended. If the tests are negative, then further HPV testing is recommended every five years. More frequent testing may be needed in some cases. The protocols used to collect, transport, and store samples vary based on both the type of HPV testing and the purpose of the testing. This should be determined in individual cases in consultation with the laboratory that will perform the testing.
Because HPV testing is often conducted concurrently with Pap testing, the most common approach uses a single sample collection within one vial for both. This approach uses liquid-based cytology (LBC). The samples are then used for Pap smear cytology as well as HPV testing and genotyping. HPV can be recognized in Pap smears by the presence of cells called koilocytes (called koilocytosis or koilocytotic atypia). Koilocytes have a hyperchromatic atypical nucleus that stains darkly and a high ratio of nuclear material to cytoplasm. There is a distinct clear appearance around the nucleus called a perinuclear halo ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?