| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
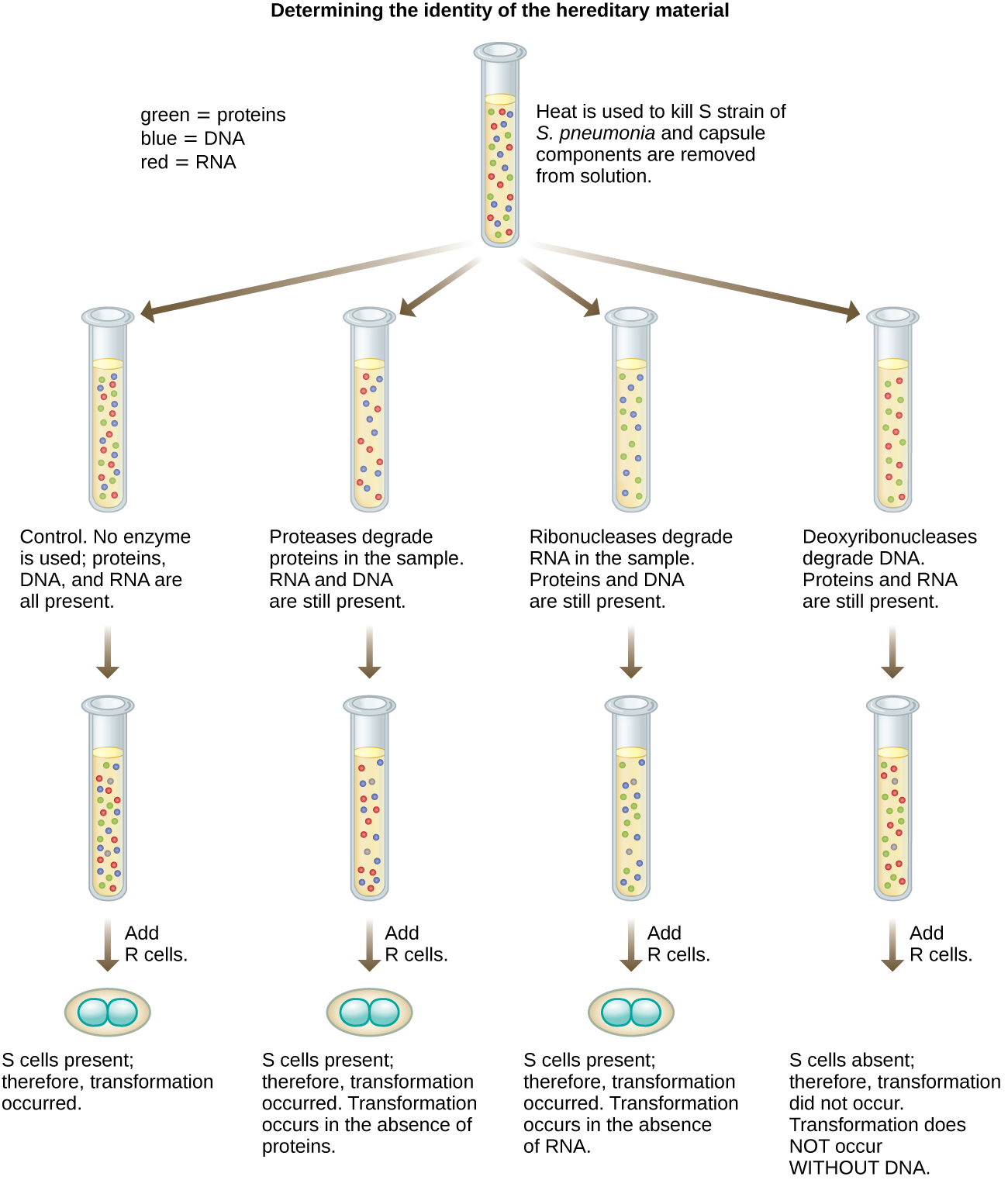
In 1944, Oswald Avery , Colin MacLeod , and Maclyn McCarty were interested in exploring Griffith’s transforming principle further. They isolated the S strain from infected dead mice, heat-killed it, and inactivated various components of the S extract, conducting a systematic elimination study ( [link] ). They used enzymes that specifically degraded proteins, RNA, and DNA and mixed the S extract with each of these individual enzymes. Then, they tested each extract/enzyme combination’s resulting ability to transform the R strain, as observed by the diffuse growth of the S strain in culture media and confirmed visually by growth on plates. They found that when DNA was degraded, the resulting mixture was no longer able to transform the R strain bacteria, whereas no other enzymatic treatment was able to prevent transformation. This led them to conclude that DNA was the transforming principle. Despite their results, many scientists did not accept their conclusion, instead believing that there were protein contaminants within their extracts.
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase performed their own experiments in 1952 and were able to provide confirmatory evidence that DNA , not protein, was the genetic material ( [link] ). A.D. Hershey, M. Chase. “Independent Functions of Viral Protein and Nucleic Acid in Growth of Bacteriophage.” Journal of General Physiology 36 no. 1 (1952):39–56. Hershey and Chase were studying a bacteriophage , a virus that infects bacteria. Viruses typically have a simple structure: a protein coat, called the capsid, and a nucleic acid core that contains the genetic material, either DNA or RNA (see Viruses ). The particular bacteriophage they were studying was the T2 bacteriophage, which infects E. coli cells. As we now know today, T2 attaches to the surface of the bacterial cell and then it injects its nucleic acids inside the cell. The phage DNA makes multiple copies of itself using the host machinery, and eventually the host cell bursts, releasing a large number of bacteriophages.
Hershey and Chase labeled the protein coat in one batch of phage using radioactive sulfur, 35 S, because sulfur is found in the amino acids methionine and cysteine but not in nucleic acids. They labeled the DNA in another batch using radioactive phosphorus, 32 P, because phosphorus is found in DNA and RNA but not typically in protein.
Each batch of phage was allowed to infect the cells separately. After infection, Hershey and Chase put each phage bacterial suspension in a blender, which detached the phage coats from the host cell, and spun down the resulting suspension in a centrifuge. The heavier bacterial cells settled down and formed a pellet, whereas the lighter phage particles stayed in the supernatant. In the tube with the protein labeled, the radioactivity remained only in the supernatant. In the tube with the DNA labeled, the radioactivity was detected only in the bacterial cells. Hershey and Chase concluded that it was the phage DNA that was injected into the cell that carried the information to produce more phage particles, thus proving that DNA, not proteins, was the source of the genetic material. As a result of their work, the scientific community more broadly accepted DNA as the molecule responsible for heredity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?