| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before the structure and function of the various components of the bacterial cell envelope were well understood, scientists were already using cell envelope characteristics to classify bacteria. In 1933, Rebecca Lancefield proposed a method for serotyping various β-hemolytic strains of Streptococcus species using an agglutination assay, a technique using the clumping of bacteria to detect specific cell-surface antigens. In doing so, Lancefield discovered that one group of S. pyogenes , found in Group A, was associated with a variety of human diseases. She determined that various strains of Group A strep could be distinguished from each other based on variations in specific cell surface proteins that she named M proteins.
Today, more than 80 different strains of Group A strep have been identified based on M proteins. Various strains of Group A strep are associated with a wide variety of human infections, including streptococcal pharyngitis ( strep throat ), impetigo , toxic shock syndrome , scarlet fever , rheumatic fever , and necrotizing fasciitis . The M protein is an important virulence factor for Group A strep, helping these strains evade the immune system. Changes in M proteins appear to alter the infectivity of a particular strain of Group A strep.
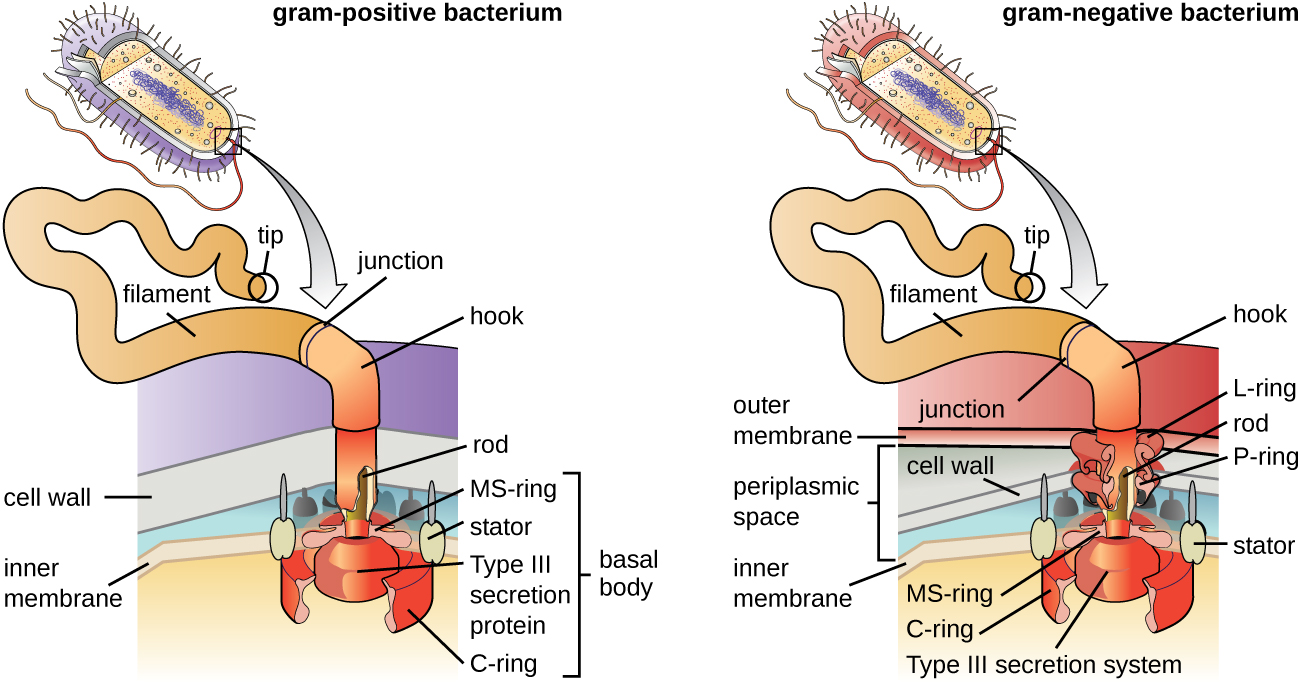
Flagella are structures used by cells to move in aqueous environments. Bacterial flagella act like propellers. They are stiff spiral filaments composed of flagellin protein subunits that extend outward from the cell and spin in solution. The basal body is the motor for the flagellum and is embedded in the plasma membrane ( [link] ). A hook region connects the basal body to the filament. Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria have different basal body configurations due to differences in cell wall structure.
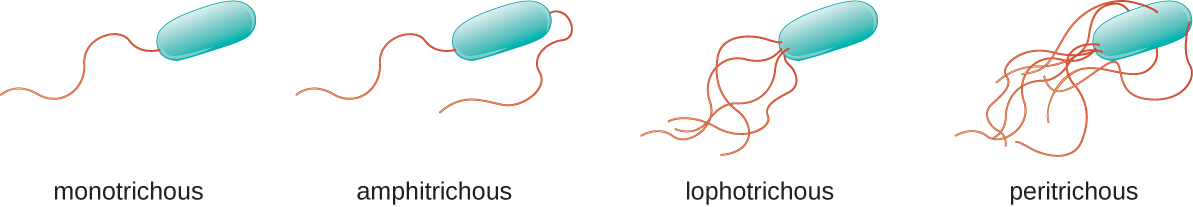
Different types of motile bacteria exhibit different arrangements of flagella ( [link] ). A bacterium with a singular flagellum, typically located at one end of the cell (polar), is said to have a monotrichous flagellum. An example of a monotrichously flagellated bacterial pathogen is Vibrio cholerae , the gram-negative bacterium that causes cholera. Cells with amphitrichous flagella have a flagellum or tufts of flagella at each end. An example is Spirillum minor , the cause of spirillary (Asian) rat-bite fever or sodoku. Cells with lophotrichous flagella have a tuft at one end of the cell. The gram-negative bacillus Pseudomonas aeruginosa , an opportunistic pathogen known for causing many infections, including “swimmer’s ear” and burn wound infections, has lophotrichous flagella. Flagella that cover the entire surface of a bacterial cell are called peritrichous flagella. The gram-negative bacterium E. coli shows a peritrichous arrangement of flagella.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?