| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
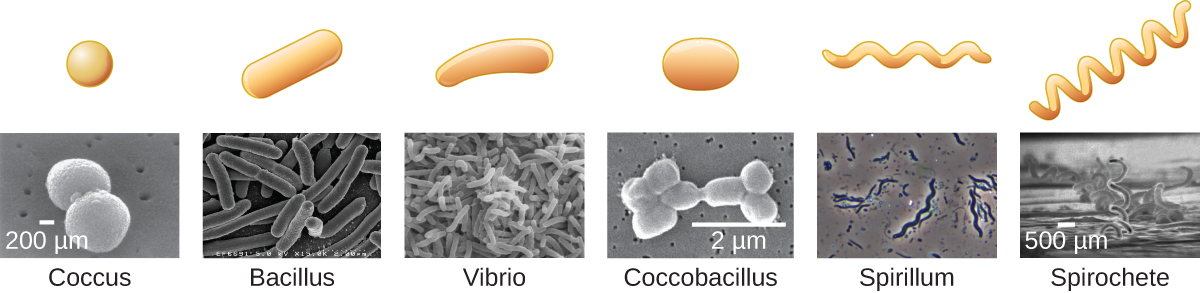
Bacteria are often described in terms of their general shape. Common shapes include spherical (coccus), rod-shaped (bacillus), or curved (spirillum, spirochete, or vibrio). [link] shows examples of these shapes.
They have a wide range of metabolic capabilities and can grow in a variety of environments, using different combinations of nutrients. Some bacteria are photosynthetic, such as oxygenic cyanobacteria and anoxygenic green sulfur and green nonsulfur bacteria; these bacteria use energy derived from sunlight, and fix carbon dioxide for growth. Other types of bacteria are nonphotosynthetic, obtaining their energy from organic or inorganic compounds in their environment.
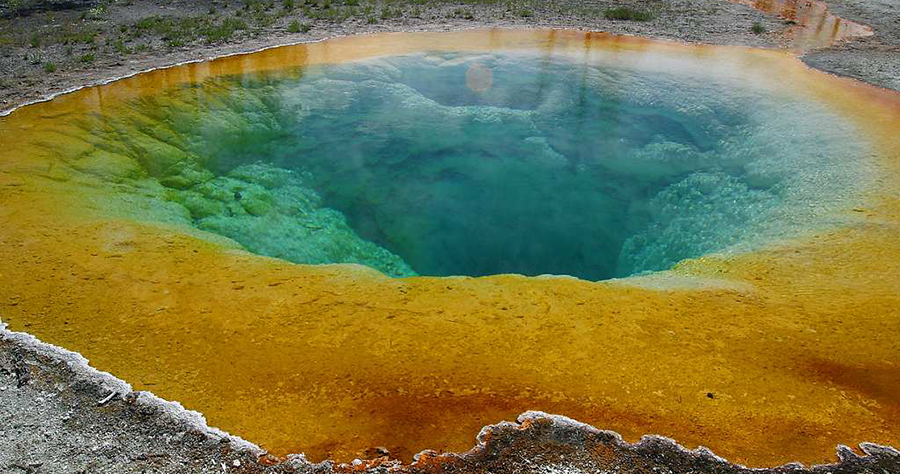
Archaea are also unicellular prokaryotic organisms. Archaea and bacteria have different evolutionary histories, as well as significant differences in genetics, metabolic pathways, and the composition of their cell walls and membranes. Unlike most bacteria, archaeal cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan, but their cell walls are often composed of a similar substance called pseudopeptidoglycan. Like bacteria, archaea are found in nearly every habitat on earth, even extreme environments that are very cold, very hot, very basic, or very acidic ( [link] ). Some archaea live in the human body, but none have been shown to be human pathogens.

The domain Eukarya contains all eukaryotes, including uni- or multicellular eukaryotes such as protists, fungi, plants, and animals. The major defining characteristic of eukaryotes is that their cells contain a nucleus.
Protist s are unicellular eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi. Algae and protozoa are examples of protists.
Algae (singular: alga) are plant-like protists that can be either unicellular or multicellular ( [link] ). Their cells are surrounded by cell walls made of cellulose, a type of carbohydrate. Algae are photosynthetic organisms that extract energy from the sun and release oxygen and carbohydrates into their environment. Because other organisms can use their waste products for energy, algae are important parts of many ecosystems. Many consumer products contain ingredients derived from algae, such as carrageenan or alginic acid, which are found in some brands of ice cream, salad dressing, beverages, lipstick, and toothpaste. A derivative of algae also plays a prominent role in the microbiology laboratory. Agar, a gel derived from algae, can be mixed with various nutrients and used to grow microorganisms in a Petri dish. Algae are also being developed as a possible source for biofuels.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?