| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
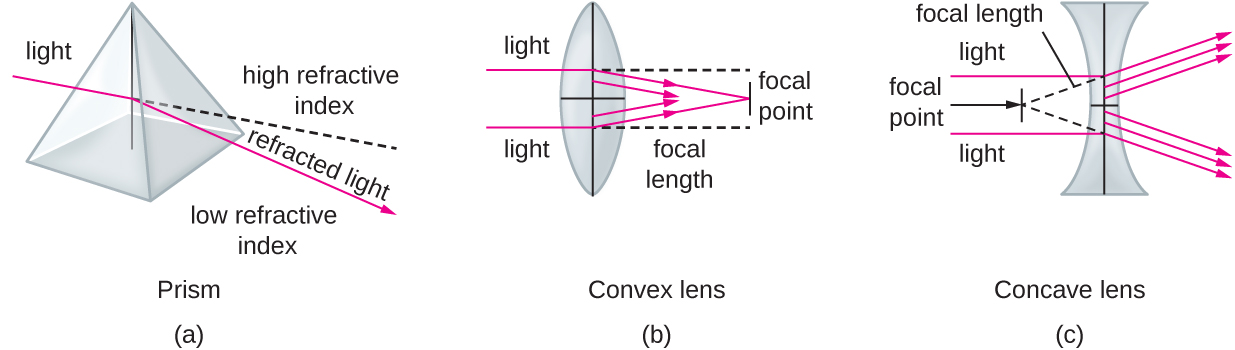
The human eye contains a lens that enables us to see images. This lens focuses the light reflecting off of objects in front of the eye onto the surface of the retina, which is like a screen in the back of the eye. Artificial lenses placed in front of the eye (contact lenses, glasses, or microscopic lenses) focus light before it is focused (again) by the lens of the eye, manipulating the image that ends up on the retina (e.g., by making it appear larger).
Images are commonly manipulated by controlling the distances between the object, the lens, and the screen, as well as the curvature of the lens. For example, for a given amount of curvature, when an object is closer to the lens, the focal points are farther from the lens. As a result, it is often necessary to manipulate these distances to create a focused image on a screen. Similarly, more curvature creates image points closer to the lens and a larger image when the image is in focus. This property is often described in terms of the focal distance, or distance to the focal point.
Visible light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) , a type of energy that is all around us. Other forms of EMR include microwaves, X-rays, and radio waves, among others. The different types of EMR fall on the electromagnetic spectrum, which is defined in terms of wavelength and frequency. The spectrum of visible light occupies a relatively small range of frequencies between infrared and ultraviolet light ( [link] ).
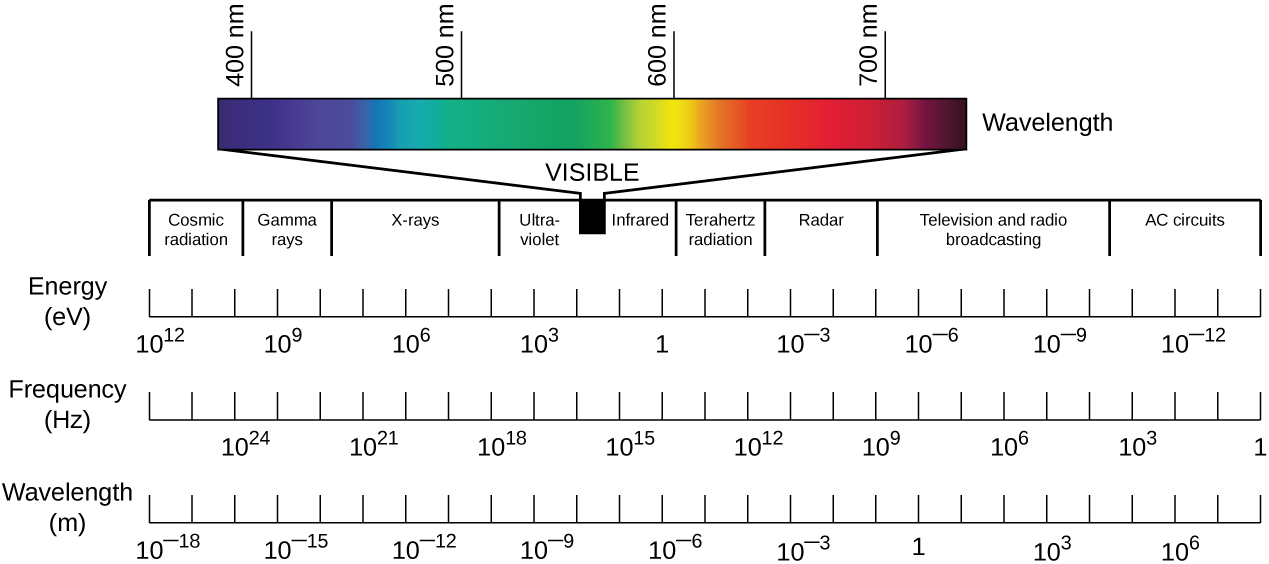
Whereas wavelength represents the distance between adjacent peaks of a light wave, frequency, in a simplified definition, represents the rate of oscillation. Waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and, therefore, have more oscillations per unit time than lower-frequency waves. Higher-frequency waves also contain more energy than lower-frequency waves. This energy is delivered as elementary particles called photons. Higher-frequency waves deliver more energetic photons than lower-frequency waves.
Photons with different energies interact differently with the retina. In the spectrum of visible light, each color corresponds to a particular frequency and wavelength ( [link] ).The lowest frequency of visible light appears as the color red, whereas the highest appears as the color violet. When the retina receives visible light of many different frequencies, we perceive this as white light. However, white light can be separated into its component colors using refraction. If we pass white light through a prism, different colors will be refracted in different directions, creating a rainbow-like spectrum on a screen behind the prism. This separation of colors is called dispersion , and it occurs because, for a given material, the refractive index is different for different frequencies of light.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?